32-5200
antibody from Invitrogen Antibodies
Targeting: NPM1
B23, NPM
 Western blot
Western blot ELISA
ELISA Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry Immunoprecipitation
Immunoprecipitation Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry Other assay
Other assayAntibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [101]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Western blot [2]
- Immunocytochemistry [2]
- Immunohistochemistry [1]
- Flow cytometry [1]
- Other assay [7]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 32-5200 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- NPM1 Monoclonal Antibody (FC-61991)
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Purifed from natural sources
- Description
- This antibody reacts with the C-terminus of Nucleophosmin (B23). Positive controls used: HeLa, K562, Jurkat, MCF-7, and HL60 cell lysates). In western blots the antibody recognizes a band at ~37 kDa.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- FC-61991
- Vial size
- 100 µg
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C
Submitted references Effects of Hydrogen Peroxide Stress on the Nucleolar Redox Environment and Pre-rRNA Maturation.
14-3-3γ prevents centrosome duplication by inhibiting NPM1 function.
Interferon-induced degradation of the persistent hepatitis B virus cccDNA form depends on ISG20.
Multiple pathways of toxicity induced by C9orf72 dipeptide repeat aggregates and G(4)C(2) RNA in a cellular model.
Acidic fibroblast growth factor underlies microenvironmental regulation of MYC in pancreatic cancer.
Accumulation of Nucleolar Inorganic Polyphosphate Is a Cellular Response to Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis.
Protein quality control in the nucleolus safeguards recovery of epigenetic regulators after heat shock.
Human AP-endonuclease (Ape1) activity on telomeric G4 structures is modulated by acetylatable lysine residues in the N-terminal sequence.
The mitochondrial outer-membrane location of the EXD2 exonuclease contradicts its direct role in nuclear DNA repair.
Overlapping roles for PARP1 and PARP2 in the recruitment of endogenous XRCC1 and PNKP into oxidized chromatin.
XRCC1 mutation is associated with PARP1 hyperactivation and cerebellar ataxia.
Epstein-Barr virus particles induce centrosome amplification and chromosomal instability.
Nuclear export factor 3 regulates localization of small nucleolar RNAs.
Multiplexed 3D super-resolution imaging of whole cells using spinning disk confocal microscopy and DNA-PAINT.
PPM1D controls nucleolar formation by up-regulating phosphorylation of nucleophosmin.
RPL23 Links Oncogenic RAS Signaling to p53-Mediated Tumor Suppression.
Expression of placenta-specific 8 in human oocytes, embryos, and models of in vitro implantation.
Functional characterization and efficient detection of Nucleophosmin/NPM1 oligomers.
Regulation of Cellular Dynamics and Chromosomal Binding Site Preference of Linker Histones H1.0 and H1.X.
14-3-3γ Prevents Centrosome Amplification and Neoplastic Progression.
Excess of NPM-ALK oncogenic signaling promotes cellular apoptosis and drug dependency.
A polybasic motif in ErbB3-binding protein 1 (EBP1) has key functions in nucleolar localization and polyphosphoinositide interaction.
Nuclear pore protein NUP88 activates anaphase-promoting complex to promote aneuploidy.
Phosphorylated STAT5 regulates p53 expression via BRCA1/BARD1-NPM1 and MDM2.
Arsenic trioxide and all-trans retinoic acid target NPM1 mutant oncoprotein levels and induce apoptosis in NPM1-mutated AML cells.
High levels of TopBP1 induce ATR-dependent shut-down of rRNA transcription and nucleolar segregation.
An RNautophagy/DNautophagy receptor, LAMP2C, possesses an arginine-rich motif that mediates RNA/DNA-binding.
Cytosolic accumulation of small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) is dynamically regulated by NADPH oxidase.
The nucleolar protein nucleophosmin is essential for autophagy induced by inhibiting Pol I transcription.
Pharmacologic inhibition of the CK2-mediated phosphorylation of B23/NPM in cancer cells selectively modulates genes related to protein synthesis, energetic metabolism, and ribosomal biogenesis.
Involvement of Nucleophosmin (NPM1/B23) in Assembly of Infectious HPV16 Capsids.
TRIM28 Is an E3 Ligase for ARF-Mediated NPM1/B23 SUMOylation That Represses Centrosome Amplification.
Cellular stress induces Bax-regulated nuclear bubble budding and rupture followed by nuclear protein release.
Nuclear interactor of ARF and Mdm2 regulates multiple pathways to activate p53.
KSHV viral cyclin interferes with T-cell development and induces lymphoma through Cdk6 and Notch activation in vivo.
Small molecule BMH-compounds that inhibit RNA polymerase I and cause nucleolar stress.
Granzyme M targets topoisomerase II alpha to trigger cell cycle arrest and caspase-dependent apoptosis.
Deregulated expression of Nucleophosmin 1 in gastric cancer and its clinicopathological implications.
mTOR signaling regulates nucleolar targeting of the SUMO-specific isopeptidase SENP3.
Replication stress is a potent driver of functional decline in ageing haematopoietic stem cells.
TP53 supports basal-like differentiation of mammary epithelial cells by preventing translocation of deltaNp63 into nucleoli.
Cdk4 and nek2 signal binucleation and centrosome amplification in a her2+ breast cancer model.
Identification of TSG101 functional domains and p21 loci required for TSG101-mediated p21 gene regulation.
The role of 3D microenvironmental organization in MCF-7 epithelial-mesenchymal transition after 7 culture days.
CRM1 and its ribosome export adaptor NMD3 localize to the nucleolus and affect rRNA synthesis.
An IKKα-nucleophosmin axis utilizes inflammatory signaling to promote genome integrity.
SET-domain bacterial effectors target heterochromatin protein 1 to activate host rDNA transcription.
Nucleophosmin/B26 regulates PTEN through interaction with HAUSP in acute myeloid leukemia.
Nucleophosmin is essential for c-Myc nucleolar localization and c-Myc-mediated rDNA transcription.
Analysis of spatial point patterns in nuclear biology.
MG63 osteoblast-like cells exhibit different behavior when grown on electrospun collagen matrix versus electrospun gelatin matrix.
Preparation and characterization of mesoporous bioactive glass/polycaprolactone nanofibrous matrix for bone tissues engineering.
DDX31 regulates the p53-HDM2 pathway and rRNA gene transcription through its interaction with NPM1 in renal cell carcinomas.
Nucleophosmin expression in renal cell carcinoma and oncocytoma.
Caveolin-1 and accelerated host aging in the breast tumor microenvironment: chemoprevention with rapamycin, an mTOR inhibitor and anti-aging drug.
Nucleolar proteins with altered expression in leukemic cell lines.
Sensitivity of tumor cells towards CIGB-300 anticancer peptide relies on its nucleolar localization.
Intracellular serine protease inhibitor SERPINB4 inhibits granzyme M-induced cell death.
Ring-like distribution of constitutive heterochromatin in bovine senescent cells.
Remodeling of ribosomal genes in somatic cells by Xenopus egg extract.
RNA helicase DDX5 is a p53-independent target of ARF that participates in ribosome biogenesis.
Nucleolar targeting of the fbw7 ubiquitin ligase by a pseudosubstrate and glycogen synthase kinase 3.
Haploinsufficiency for ribosomal protein genes causes selective activation of p53 in human erythroid progenitor cells.
The SUMO system controls nucleolar partitioning of a novel mammalian ribosome biogenesis complex.
The enigmatic role of nucleophosmin in malignant melanoma: does it have an effect?
The balance between rRNA and ribosomal protein synthesis up- and downregulates the tumour suppressor p53 in mammalian cells.
Identification of nuclear phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate-interacting proteins by neomycin extraction.
The role of RPGR in cilia formation and actin stability.
Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 regulates multiple myeloma cell growth and bortezomib-induced cell death.
ARF suppresses tumor angiogenesis through translational control of VEGFA mRNA.
PHF8 is a histone H3K9me2 demethylase regulating rRNA synthesis.
Extensive crosstalk between O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation regulates cytokinesis.
Ribosome-associated nucleophosmin 1: increased expression and shuttling activity distinguishes prognostic subtypes in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.
Critical lysine residues within the overlooked N-terminal domain of human APE1 regulate its biological functions.
TIPT2 and geminin interact with basal transcription factors to synergize in transcriptional regulation.
B23 interacts with PES1 and is involved in nucleolar localization of PES1.
Human Dna2 is a nuclear and mitochondrial DNA maintenance protein.
APE1/Ref-1 interacts with NPM1 within nucleoli and plays a role in the rRNA quality control process.
Segmentation of fluorescence microscopy images for quantitative analysis of cell nuclear architecture.
Residues in the alternative reading frame tumor suppressor that influence its stability and p53-independent activities.
DNA damage-dependent translocation of B23 and p19 ARF is regulated by the Jun N-terminal kinase pathway.
Mitochondrial p32 is a critical mediator of ARF-induced apoptosis.
Alternative mRNA splicing of SAP30L regulates its transcriptional repression activity.
A non-tumor suppressor role for basal p19ARF in maintaining nucleolar structure and function.
RBM19 is essential for preimplantation development in the mouse.
Binding to nucleophosmin determines the localization of human and chicken ARF but not its impact on p53.
JHDM1B/FBXL10 is a nucleolar protein that represses transcription of ribosomal RNA genes.
Proteome analysis of proliferative response of bystander cells adjacent to cells exposed to ionizing radiation.
Adeno-associated virus interactions with B23/Nucleophosmin: identification of sub-nucleolar virion regions.
Global functional analysis of nucleophosmin in Taxol response, cancer, chromatin regulation, and ribosomal DNA transcription.
SAP30L interacts with members of the Sin3A corepressor complex and targets Sin3A to the nucleolus.
Immunohistochemistry predicts nucleophosmin (NPM) mutations in acute myeloid leukemia.
Hepatitis C virus core protein recruits nucleolar phosphoprotein B23 and coactivator p300 to relieve the repression effect of transcriptional factor YY1 on B23 gene expression.
Increased levels of the FoxM1 transcription factor accelerate development and progression of prostate carcinomas in both TRAMP and LADY transgenic mice.
Sumoylation induced by the Arf tumor suppressor: a p53-independent function.
Free cholesterol-loaded macrophages are an abundant source of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6: model of NF-kappaB- and map kinase-dependent inflammation in advanced atherosclerosis.
Nucleophosmin (B23) targets ARF to nucleoli and inhibits its function.
Proteomic characterization of oxidative dysfunction in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) induced by exposure to oxidized LDL.
Temporal and spatial control of nucleophosmin by the Ran-Crm1 complex in centrosome duplication.
Proteomic analysis reveals hyperactivation of the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway in neurofibromatosis 1-associated human and mouse brain tumors.
Cyclin G1 has growth inhibitory activity linked to the ARF-Mdm2-p53 and pRb tumor suppressor pathways.
Sapio RT, Burns CJ, Pestov DG
Frontiers in molecular biosciences 2021;8:678488
Frontiers in molecular biosciences 2021;8:678488
14-3-3γ prevents centrosome duplication by inhibiting NPM1 function.
Bose A, Modi K, Dey S, Dalvi S, Nadkarni P, Sudarshan M, Kundu TK, Venkatraman P, Dalal SN
Genes to cells : devoted to molecular & cellular mechanisms 2021 Jun;26(6):426-446
Genes to cells : devoted to molecular & cellular mechanisms 2021 Jun;26(6):426-446
Interferon-induced degradation of the persistent hepatitis B virus cccDNA form depends on ISG20.
Stadler D, Kächele M, Jones AN, Hess J, Urban C, Schneider J, Xia Y, Oswald A, Nebioglu F, Bester R, Lasitschka F, Ringelhan M, Ko C, Chou WM, Geerlof A, van de Klundert MA, Wettengel JM, Schirmacher P, Heikenwälder M, Schreiner S, Bartenschlager R, Pichlmair A, Sattler M, Unger K, Protzer U
EMBO reports 2021 Jun 4;22(6):e49568
EMBO reports 2021 Jun 4;22(6):e49568
Multiple pathways of toxicity induced by C9orf72 dipeptide repeat aggregates and G(4)C(2) RNA in a cellular model.
Frottin F, Pérez-Berlanga M, Hartl FU, Hipp MS
eLife 2021 Jun 23;10
eLife 2021 Jun 23;10
Acidic fibroblast growth factor underlies microenvironmental regulation of MYC in pancreatic cancer.
Bhattacharyya S, Oon C, Kothari A, Horton W, Link J, Sears RC, Sherman MH
The Journal of experimental medicine 2020 Aug 3;217(8)
The Journal of experimental medicine 2020 Aug 3;217(8)
Accumulation of Nucleolar Inorganic Polyphosphate Is a Cellular Response to Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis.
Xie L, Rajpurkar A, Quarles E, Taube N, Rai AS, Erba J, Sliwinski B, Markowitz M, Jakob U, Knoefler D
Frontiers in oncology 2019;9:1410
Frontiers in oncology 2019;9:1410
Protein quality control in the nucleolus safeguards recovery of epigenetic regulators after heat shock.
Azkanaz M, Rodríguez López A, de Boer B, Huiting W, Angrand PO, Vellenga E, Kampinga HH, Bergink S, Martens JH, Schuringa JJ, van den Boom V
eLife 2019 Jun 14;8
eLife 2019 Jun 14;8
Human AP-endonuclease (Ape1) activity on telomeric G4 structures is modulated by acetylatable lysine residues in the N-terminal sequence.
Burra S, Marasco D, Malfatti MC, Antoniali G, Virgilio A, Esposito V, Demple B, Galeone A, Tell G
DNA repair 2019 Jan;73:129-143
DNA repair 2019 Jan;73:129-143
The mitochondrial outer-membrane location of the EXD2 exonuclease contradicts its direct role in nuclear DNA repair.
Hensen F, Moretton A, van Esveld S, Farge G, Spelbrink JN
Scientific reports 2018 Mar 29;8(1):5368
Scientific reports 2018 Mar 29;8(1):5368
Overlapping roles for PARP1 and PARP2 in the recruitment of endogenous XRCC1 and PNKP into oxidized chromatin.
Hanzlikova H, Gittens W, Krejcikova K, Zeng Z, Caldecott KW
Nucleic acids research 2017 Mar 17;45(5):2546-2557
Nucleic acids research 2017 Mar 17;45(5):2546-2557
XRCC1 mutation is associated with PARP1 hyperactivation and cerebellar ataxia.
Hoch NC, Hanzlikova H, Rulten SL, Tétreault M, Komulainen E, Ju L, Hornyak P, Zeng Z, Gittens W, Rey SA, Staras K, Mancini GM, McKinnon PJ, Wang ZQ, Wagner JD, Care4Rare Canada Consortium, Yoon G, Caldecott KW
Nature 2017 Jan 5;541(7635):87-91
Nature 2017 Jan 5;541(7635):87-91
Epstein-Barr virus particles induce centrosome amplification and chromosomal instability.
Shumilov A, Tsai MH, Schlosser YT, Kratz AS, Bernhardt K, Fink S, Mizani T, Lin X, Jauch A, Mautner J, Kopp-Schneider A, Feederle R, Hoffmann I, Delecluse HJ
Nature communications 2017 Feb 10;8:14257
Nature communications 2017 Feb 10;8:14257
Nuclear export factor 3 regulates localization of small nucleolar RNAs.
Li MW, Sletten AC, Lee J, Pyles KD, Matkovich SJ, Ory DS, Schaffer JE
The Journal of biological chemistry 2017 Dec 8;292(49):20228-20239
The Journal of biological chemistry 2017 Dec 8;292(49):20228-20239
Multiplexed 3D super-resolution imaging of whole cells using spinning disk confocal microscopy and DNA-PAINT.
Schueder F, Lara-Gutiérrez J, Beliveau BJ, Saka SK, Sasaki HM, Woehrstein JB, Strauss MT, Grabmayr H, Yin P, Jungmann R
Nature communications 2017 Dec 12;8(1):2090
Nature communications 2017 Dec 12;8(1):2090
PPM1D controls nucleolar formation by up-regulating phosphorylation of nucleophosmin.
Kozakai Y, Kamada R, Furuta J, Kiyota Y, Chuman Y, Sakaguchi K
Scientific reports 2016 Sep 13;6:33272
Scientific reports 2016 Sep 13;6:33272
RPL23 Links Oncogenic RAS Signaling to p53-Mediated Tumor Suppression.
Meng X, Tackmann NR, Liu S, Yang J, Dong J, Wu C, Cox AD, Zhang Y
Cancer research 2016 Sep 1;76(17):5030-9
Cancer research 2016 Sep 1;76(17):5030-9
Expression of placenta-specific 8 in human oocytes, embryos, and models of in vitro implantation.
Li M, Liu D, Wang L, Wang W, Wang A, Yao Y
Fertility and sterility 2016 Sep 1;106(3):781-789.e2
Fertility and sterility 2016 Sep 1;106(3):781-789.e2
Functional characterization and efficient detection of Nucleophosmin/NPM1 oligomers.
Lin J, Hisaoka M, Nagata K, Okuwaki M
Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2016 Nov 25;480(4):702-708
Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2016 Nov 25;480(4):702-708
Regulation of Cellular Dynamics and Chromosomal Binding Site Preference of Linker Histones H1.0 and H1.X.
Okuwaki M, Abe M, Hisaoka M, Nagata K
Molecular and cellular biology 2016 Nov 1;36(21):2681-2696
Molecular and cellular biology 2016 Nov 1;36(21):2681-2696
14-3-3γ Prevents Centrosome Amplification and Neoplastic Progression.
Mukhopadhyay A, Sehgal L, Bose A, Gulvady A, Senapati P, Thorat R, Basu S, Bhatt K, Hosing AS, Balyan R, Borde L, Kundu TK, Dalal SN
Scientific reports 2016 Jun 2;6:26580
Scientific reports 2016 Jun 2;6:26580
Excess of NPM-ALK oncogenic signaling promotes cellular apoptosis and drug dependency.
Ceccon M, Merlo MEB, Mologni L, Poggio T, Varesio LM, Menotti M, Bombelli S, Rigolio R, Manazza AD, Di Giacomo F, Ambrogio C, Giudici G, Casati C, Mastini C, Compagno M, Turner SD, Gambacorti-Passerini C, Chiarle R, Voena C
Oncogene 2016 Jul 21;35(29):3854-3865
Oncogene 2016 Jul 21;35(29):3854-3865
A polybasic motif in ErbB3-binding protein 1 (EBP1) has key functions in nucleolar localization and polyphosphoinositide interaction.
Karlsson T, Altankhuyag A, Dobrovolska O, Turcu DC, Lewis AE
The Biochemical journal 2016 Jul 15;473(14):2033-47
The Biochemical journal 2016 Jul 15;473(14):2033-47
Nuclear pore protein NUP88 activates anaphase-promoting complex to promote aneuploidy.
Naylor RM, Jeganathan KB, Cao X, van Deursen JM
The Journal of clinical investigation 2016 Feb;126(2):543-59
The Journal of clinical investigation 2016 Feb;126(2):543-59
Phosphorylated STAT5 regulates p53 expression via BRCA1/BARD1-NPM1 and MDM2.
Ren Z, Aerts JL, Vandenplas H, Wang JA, Gorbenko O, Chen JP, Giron P, Heirman C, Goyvaerts C, Zacksenhaus E, Minden MD, Stambolic V, Breckpot K, De Grève J
Cell death & disease 2016 Dec 22;7(12):e2560
Cell death & disease 2016 Dec 22;7(12):e2560
Arsenic trioxide and all-trans retinoic acid target NPM1 mutant oncoprotein levels and induce apoptosis in NPM1-mutated AML cells.
Martelli MP, Gionfriddo I, Mezzasoma F, Milano F, Pierangeli S, Mulas F, Pacini R, Tabarrini A, Pettirossi V, Rossi R, Vetro C, Brunetti L, Sportoletti P, Tiacci E, Di Raimondo F, Falini B
Blood 2015 May 28;125(22):3455-65
Blood 2015 May 28;125(22):3455-65
High levels of TopBP1 induce ATR-dependent shut-down of rRNA transcription and nucleolar segregation.
Sokka M, Rilla K, Miinalainen I, Pospiech H, Syväoja JE
Nucleic acids research 2015 May 26;43(10):4975-89
Nucleic acids research 2015 May 26;43(10):4975-89
An RNautophagy/DNautophagy receptor, LAMP2C, possesses an arginine-rich motif that mediates RNA/DNA-binding.
Fujiwara Y, Hase K, Wada K, Kabuta T
Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2015 May 1;460(2):281-6
Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2015 May 1;460(2):281-6
Cytosolic accumulation of small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) is dynamically regulated by NADPH oxidase.
Holley CL, Li MW, Scruggs BS, Matkovich SJ, Ory DS, Schaffer JE
The Journal of biological chemistry 2015 May 1;290(18):11741-8
The Journal of biological chemistry 2015 May 1;290(18):11741-8
The nucleolar protein nucleophosmin is essential for autophagy induced by inhibiting Pol I transcription.
Katagiri N, Kuroda T, Kishimoto H, Hayashi Y, Kumazawa T, Kimura K
Scientific reports 2015 Mar 10;5:8903
Scientific reports 2015 Mar 10;5:8903
Pharmacologic inhibition of the CK2-mediated phosphorylation of B23/NPM in cancer cells selectively modulates genes related to protein synthesis, energetic metabolism, and ribosomal biogenesis.
Perera Y, Pedroso S, Borras-Hidalgo O, Vázquez DM, Miranda J, Villareal A, Falcón V, Cruz LD, Farinas HG, Perea SE
Molecular and cellular biochemistry 2015 Jun;404(1-2):103-12
Molecular and cellular biochemistry 2015 Jun;404(1-2):103-12
Involvement of Nucleophosmin (NPM1/B23) in Assembly of Infectious HPV16 Capsids.
Day PM, Thompson CD, Pang YY, Lowy DR, Schiller JT
Papillomavirus research (Amsterdam, Netherlands) 2015 Dec;1:74-89
Papillomavirus research (Amsterdam, Netherlands) 2015 Dec;1:74-89
TRIM28 Is an E3 Ligase for ARF-Mediated NPM1/B23 SUMOylation That Represses Centrosome Amplification.
Neo SH, Itahana Y, Alagu J, Kitagawa M, Guo AK, Lee SH, Tang K, Itahana K
Molecular and cellular biology 2015 Aug;35(16):2851-63
Molecular and cellular biology 2015 Aug;35(16):2851-63
Cellular stress induces Bax-regulated nuclear bubble budding and rupture followed by nuclear protein release.
Lindenboim L, Sasson T, Worman HJ, Borner C, Stein R
Nucleus (Austin, Tex.) 2014;5(6):527-41
Nucleus (Austin, Tex.) 2014;5(6):527-41
Nuclear interactor of ARF and Mdm2 regulates multiple pathways to activate p53.
Reed SM, Hagen J, Tompkins VS, Thies K, Quelle FW, Quelle DE
Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.) 2014;13(8):1288-98
Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.) 2014;13(8):1288-98
KSHV viral cyclin interferes with T-cell development and induces lymphoma through Cdk6 and Notch activation in vivo.
Pekkonen P, Järviluoma A, Zinovkina N, Cvrljevic A, Prakash S, Westermarck J, Evan GI, Cesarman E, Verschuren EW, Ojala PM
Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.) 2014;13(23):3670-84
Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.) 2014;13(23):3670-84
Small molecule BMH-compounds that inhibit RNA polymerase I and cause nucleolar stress.
Peltonen K, Colis L, Liu H, Jäämaa S, Zhang Z, Af Hällström T, Moore HM, Sirajuddin P, Laiho M
Molecular cancer therapeutics 2014 Nov;13(11):2537-46
Molecular cancer therapeutics 2014 Nov;13(11):2537-46
Granzyme M targets topoisomerase II alpha to trigger cell cycle arrest and caspase-dependent apoptosis.
de Poot SA, Lai KW, van der Wal L, Plasman K, Van Damme P, Porter AC, Gevaert K, Bovenschen N
Cell death and differentiation 2014 Mar;21(3):416-26
Cell death and differentiation 2014 Mar;21(3):416-26
Deregulated expression of Nucleophosmin 1 in gastric cancer and its clinicopathological implications.
Leal MF, Mazzotti TK, Calcagno DQ, Cirilo PD, Martinez MC, Demachki S, Assumpção PP, Chammas R, Burbano RR, Smith MC
BMC gastroenterology 2014 Jan 10;14:9
BMC gastroenterology 2014 Jan 10;14:9
mTOR signaling regulates nucleolar targeting of the SUMO-specific isopeptidase SENP3.
Raman N, Nayak A, Muller S
Molecular and cellular biology 2014 Dec;34(24):4474-84
Molecular and cellular biology 2014 Dec;34(24):4474-84
Replication stress is a potent driver of functional decline in ageing haematopoietic stem cells.
Flach J, Bakker ST, Mohrin M, Conroy PC, Pietras EM, Reynaud D, Alvarez S, Diolaiti ME, Ugarte F, Forsberg EC, Le Beau MM, Stohr BA, Méndez J, Morrison CG, Passegué E
Nature 2014 Aug 14;512(7513):198-202
Nature 2014 Aug 14;512(7513):198-202
TP53 supports basal-like differentiation of mammary epithelial cells by preventing translocation of deltaNp63 into nucleoli.
Munne PM, Gu Y, Tumiati M, Gao P, Koopal S, Uusivirta S, Sawicki J, Wei GH, Kuznetsov SG
Scientific reports 2014 Apr 11;4:4663
Scientific reports 2014 Apr 11;4:4663
Cdk4 and nek2 signal binucleation and centrosome amplification in a her2+ breast cancer model.
Harrison Pitner MK, Saavedra HI
PloS one 2013;8(6):e65971
PloS one 2013;8(6):e65971
Identification of TSG101 functional domains and p21 loci required for TSG101-mediated p21 gene regulation.
Lin YS, Chen YJ, Cohen SN, Cheng TH
PloS one 2013;8(11):e79674
PloS one 2013;8(11):e79674
The role of 3D microenvironmental organization in MCF-7 epithelial-mesenchymal transition after 7 culture days.
Foroni L, Vasuri F, Valente S, Gualandi C, Focarete ML, Caprara G, Scandola M, D'Errico-Grigioni A, Pasquinelli G
Experimental cell research 2013 Jun 10;319(10):1515-22
Experimental cell research 2013 Jun 10;319(10):1515-22
CRM1 and its ribosome export adaptor NMD3 localize to the nucleolus and affect rRNA synthesis.
Bai B, Moore HM, Laiho M
Nucleus (Austin, Tex.) 2013 Jul-Aug;4(4):315-25
Nucleus (Austin, Tex.) 2013 Jul-Aug;4(4):315-25
An IKKα-nucleophosmin axis utilizes inflammatory signaling to promote genome integrity.
Xia X, Liu S, Xiao Z, Zhu F, Song NY, Zhou M, Liu B, Shen J, Nagashima K, Veenstra TD, Burkett S, Datla M, Willette-Brown J, Shen H, Hu Y
Cell reports 2013 Dec 12;5(5):1243-55
Cell reports 2013 Dec 12;5(5):1243-55
SET-domain bacterial effectors target heterochromatin protein 1 to activate host rDNA transcription.
Li T, Lu Q, Wang G, Xu H, Huang H, Cai T, Kan B, Ge J, Shao F
EMBO reports 2013 Aug;14(8):733-40
EMBO reports 2013 Aug;14(8):733-40
Nucleophosmin/B26 regulates PTEN through interaction with HAUSP in acute myeloid leukemia.
Noguera NI, Song MS, Divona M, Catalano G, Calvo KL, García F, Ottone T, Florenzano F, Faraoni I, Battistini L, Colombo E, Amadori S, Pandolfi PP, Lo-Coco F
Leukemia 2013 Apr;27(5):1037-43
Leukemia 2013 Apr;27(5):1037-43
Nucleophosmin is essential for c-Myc nucleolar localization and c-Myc-mediated rDNA transcription.
Li Z, Hann SR
Oncogene 2013 Apr 11;32(15):1988-94
Oncogene 2013 Apr 11;32(15):1988-94
Analysis of spatial point patterns in nuclear biology.
Weston DJ, Adams NM, Russell RA, Stephens DA, Freemont PS
PloS one 2012;7(5):e36841
PloS one 2012;7(5):e36841
MG63 osteoblast-like cells exhibit different behavior when grown on electrospun collagen matrix versus electrospun gelatin matrix.
Tsai SW, Liou HM, Lin CJ, Kuo KL, Hung YS, Weng RC, Hsu FY
PloS one 2012;7(2):e31200
PloS one 2012;7(2):e31200
Preparation and characterization of mesoporous bioactive glass/polycaprolactone nanofibrous matrix for bone tissues engineering.
Lin HM, Lin YH, Hsu FY
Journal of materials science. Materials in medicine 2012 Nov;23(11):2619-30
Journal of materials science. Materials in medicine 2012 Nov;23(11):2619-30
DDX31 regulates the p53-HDM2 pathway and rRNA gene transcription through its interaction with NPM1 in renal cell carcinomas.
Fukawa T, Ono M, Matsuo T, Uehara H, Miki T, Nakamura Y, Kanayama HO, Katagiri T
Cancer research 2012 Nov 15;72(22):5867-77
Cancer research 2012 Nov 15;72(22):5867-77
Nucleophosmin expression in renal cell carcinoma and oncocytoma.
Sari A, Calli A, Altinboga AA, Pehlivan FS, Gorgel SN, Balci U, Ermete M, Dincel C, Cakalagaoglu F
APMIS : acta pathologica, microbiologica, et immunologica Scandinavica 2012 Mar;120(3):187-94
APMIS : acta pathologica, microbiologica, et immunologica Scandinavica 2012 Mar;120(3):187-94
Caveolin-1 and accelerated host aging in the breast tumor microenvironment: chemoprevention with rapamycin, an mTOR inhibitor and anti-aging drug.
Mercier I, Camacho J, Titchen K, Gonzales DM, Quann K, Bryant KG, Molchansky A, Milliman JN, Whitaker-Menezes D, Sotgia F, Jasmin JF, Schwarting R, Pestell RG, Blagosklonny MV, Lisanti MP
The American journal of pathology 2012 Jul;181(1):278-93
The American journal of pathology 2012 Jul;181(1):278-93
Nucleolar proteins with altered expression in leukemic cell lines.
Teittinen KJ, Kärkkäinen P, Salonen J, Rönnholm G, Korkeamäki H, Vihinen M, Kalkkinen N, Lohi O
Leukemia research 2012 Feb;36(2):232-6
Leukemia research 2012 Feb;36(2):232-6
Sensitivity of tumor cells towards CIGB-300 anticancer peptide relies on its nucleolar localization.
Perera Y, Costales HC, Diaz Y, Reyes O, Farina HG, Mendez L, Gómez RE, Acevedo BE, Gomez DE, Alonso DF, Perea SE
Journal of peptide science : an official publication of the European Peptide Society 2012 Apr;18(4):215-23
Journal of peptide science : an official publication of the European Peptide Society 2012 Apr;18(4):215-23
Intracellular serine protease inhibitor SERPINB4 inhibits granzyme M-induced cell death.
de Koning PJ, Kummer JA, de Poot SA, Quadir R, Broekhuizen R, McGettrick AF, Higgins WJ, Devreese B, Worrall DM, Bovenschen N
PloS one 2011;6(8):e22645
PloS one 2011;6(8):e22645
Ring-like distribution of constitutive heterochromatin in bovine senescent cells.
Pichugin A, Beaujean N, Vignon X, Vassetzky Y
PloS one 2011;6(11):e26844
PloS one 2011;6(11):e26844
Remodeling of ribosomal genes in somatic cells by Xenopus egg extract.
Østrup O, Hyttel P, Klærke DA, Collas P
Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2011 Sep 2;412(3):487-93
Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2011 Sep 2;412(3):487-93
RNA helicase DDX5 is a p53-independent target of ARF that participates in ribosome biogenesis.
Saporita AJ, Chang HC, Winkeler CL, Apicelli AJ, Kladney RD, Wang J, Townsend RR, Michel LS, Weber JD
Cancer research 2011 Nov 1;71(21):6708-17
Cancer research 2011 Nov 1;71(21):6708-17
Nucleolar targeting of the fbw7 ubiquitin ligase by a pseudosubstrate and glycogen synthase kinase 3.
Welcker M, Larimore EA, Frappier L, Clurman BE
Molecular and cellular biology 2011 Mar;31(6):1214-24
Molecular and cellular biology 2011 Mar;31(6):1214-24
Haploinsufficiency for ribosomal protein genes causes selective activation of p53 in human erythroid progenitor cells.
Dutt S, Narla A, Lin K, Mullally A, Abayasekara N, Megerdichian C, Wilson FH, Currie T, Khanna-Gupta A, Berliner N, Kutok JL, Ebert BL
Blood 2011 Mar 3;117(9):2567-76
Blood 2011 Mar 3;117(9):2567-76
The SUMO system controls nucleolar partitioning of a novel mammalian ribosome biogenesis complex.
Finkbeiner E, Haindl M, Muller S
The EMBO journal 2011 Mar 16;30(6):1067-78
The EMBO journal 2011 Mar 16;30(6):1067-78
The enigmatic role of nucleophosmin in malignant melanoma: does it have an effect?
Calli AO, Sari A, Evcim G, Altinboga A, Sadullahoglu C, Ermete M
Indian journal of pathology & microbiology 2011 Jul-Sep;54(3):482-6
Indian journal of pathology & microbiology 2011 Jul-Sep;54(3):482-6
The balance between rRNA and ribosomal protein synthesis up- and downregulates the tumour suppressor p53 in mammalian cells.
Donati G, Bertoni S, Brighenti E, Vici M, Treré D, Volarevic S, Montanaro L, Derenzini M
Oncogene 2011 Jul 21;30(29):3274-88
Oncogene 2011 Jul 21;30(29):3274-88
Identification of nuclear phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate-interacting proteins by neomycin extraction.
Lewis AE, Sommer L, Arntzen MØ, Strahm Y, Morrice NA, Divecha N, D'Santos CS
Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP 2011 Feb;10(2):M110.003376
Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP 2011 Feb;10(2):M110.003376
The role of RPGR in cilia formation and actin stability.
Gakovic M, Shu X, Kasioulis I, Carpanini S, Moraga I, Wright AF
Human molecular genetics 2011 Dec 15;20(24):4840-50
Human molecular genetics 2011 Dec 15;20(24):4840-50
Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 regulates multiple myeloma cell growth and bortezomib-induced cell death.
Piazza F, Manni S, Tubi LQ, Montini B, Pavan L, Colpo A, Gnoato M, Cabrelle A, Adami F, Zambello R, Trentin L, Gurrieri C, Semenzato G
BMC cancer 2010 Oct 4;10:526
BMC cancer 2010 Oct 4;10:526
ARF suppresses tumor angiogenesis through translational control of VEGFA mRNA.
Kawagishi H, Nakamura H, Maruyama M, Mizutani S, Sugimoto K, Takagi M, Sugimoto M
Cancer research 2010 Jun 1;70(11):4749-58
Cancer research 2010 Jun 1;70(11):4749-58
PHF8 is a histone H3K9me2 demethylase regulating rRNA synthesis.
Zhu Z, Wang Y, Li X, Wang Y, Xu L, Wang X, Sun T, Dong X, Chen L, Mao H, Yu Y, Li J, Chen PA, Chen CD
Cell research 2010 Jul;20(7):794-801
Cell research 2010 Jul;20(7):794-801
Extensive crosstalk between O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation regulates cytokinesis.
Wang Z, Udeshi ND, Slawson C, Compton PD, Sakabe K, Cheung WD, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Hart GW
Science signaling 2010 Jan 12;3(104):ra2
Science signaling 2010 Jan 12;3(104):ra2
Ribosome-associated nucleophosmin 1: increased expression and shuttling activity distinguishes prognostic subtypes in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.
Rees-Unwin KS, Faragher R, Unwin RD, Adams J, Brown PJ, Buckle AM, Pettitt A, Hutchinson CV, Johnson SM, Pulford K, Banham AH, Whetton AD, Lucas G, Mason DY, Burthem J
British journal of haematology 2010 Feb;148(4):534-43
British journal of haematology 2010 Feb;148(4):534-43
Critical lysine residues within the overlooked N-terminal domain of human APE1 regulate its biological functions.
Fantini D, Vascotto C, Marasco D, D'Ambrosio C, Romanello M, Vitagliano L, Pedone C, Poletto M, Cesaratto L, Quadrifoglio F, Scaloni A, Radicella JP, Tell G
Nucleic acids research 2010 Dec;38(22):8239-56
Nucleic acids research 2010 Dec;38(22):8239-56
TIPT2 and geminin interact with basal transcription factors to synergize in transcriptional regulation.
Pitulescu ME, Teichmann M, Luo L, Kessel M
BMC biochemistry 2009 Jun 10;10:16
BMC biochemistry 2009 Jun 10;10:16
B23 interacts with PES1 and is involved in nucleolar localization of PES1.
Zhang J, Yang Y, Wu J
Acta biochimica et biophysica Sinica 2009 Dec;41(12):991-7
Acta biochimica et biophysica Sinica 2009 Dec;41(12):991-7
Human Dna2 is a nuclear and mitochondrial DNA maintenance protein.
Duxin JP, Dao B, Martinsson P, Rajala N, Guittat L, Campbell JL, Spelbrink JN, Stewart SA
Molecular and cellular biology 2009 Aug;29(15):4274-82
Molecular and cellular biology 2009 Aug;29(15):4274-82
APE1/Ref-1 interacts with NPM1 within nucleoli and plays a role in the rRNA quality control process.
Vascotto C, Fantini D, Romanello M, Cesaratto L, Deganuto M, Leonardi A, Radicella JP, Kelley MR, D'Ambrosio C, Scaloni A, Quadrifoglio F, Tell G
Molecular and cellular biology 2009 Apr;29(7):1834-54
Molecular and cellular biology 2009 Apr;29(7):1834-54
Segmentation of fluorescence microscopy images for quantitative analysis of cell nuclear architecture.
Russell RA, Adams NM, Stephens DA, Batty E, Jensen K, Freemont PS
Biophysical journal 2009 Apr 22;96(8):3379-89
Biophysical journal 2009 Apr 22;96(8):3379-89
Residues in the alternative reading frame tumor suppressor that influence its stability and p53-independent activities.
di Tommaso A, Hagen J, Tompkins V, Muniz V, Dudakovic A, Kitzis A, Ladeveze V, Quelle DE
Experimental cell research 2009 Apr 15;315(7):1326-35
Experimental cell research 2009 Apr 15;315(7):1326-35
DNA damage-dependent translocation of B23 and p19 ARF is regulated by the Jun N-terminal kinase pathway.
Yogev O, Saadon K, Anzi S, Inoue K, Shaulian E
Cancer research 2008 Mar 1;68(5):1398-406
Cancer research 2008 Mar 1;68(5):1398-406
Mitochondrial p32 is a critical mediator of ARF-induced apoptosis.
Itahana K, Zhang Y
Cancer cell 2008 Jun;13(6):542-53
Cancer cell 2008 Jun;13(6):542-53
Alternative mRNA splicing of SAP30L regulates its transcriptional repression activity.
Korkeamäki H, Viiri K, Kukkonen MK, Mäki M, Lohi O
FEBS letters 2008 Jan 23;582(2):379-84
FEBS letters 2008 Jan 23;582(2):379-84
A non-tumor suppressor role for basal p19ARF in maintaining nucleolar structure and function.
Apicelli AJ, Maggi LB Jr, Hirbe AC, Miceli AP, Olanich ME, Schulte-Winkeler CL, Saporita AJ, Kuchenreuther M, Sanchez J, Weilbaecher K, Weber JD
Molecular and cellular biology 2008 Feb;28(3):1068-80
Molecular and cellular biology 2008 Feb;28(3):1068-80
RBM19 is essential for preimplantation development in the mouse.
Zhang J, Tomasini AJ, Mayer AN
BMC developmental biology 2008 Dec 16;8:115
BMC developmental biology 2008 Dec 16;8:115
Binding to nucleophosmin determines the localization of human and chicken ARF but not its impact on p53.
Moulin S, Llanos S, Kim SH, Peters G
Oncogene 2008 Apr 10;27(17):2382-9
Oncogene 2008 Apr 10;27(17):2382-9
JHDM1B/FBXL10 is a nucleolar protein that represses transcription of ribosomal RNA genes.
Frescas D, Guardavaccaro D, Bassermann F, Koyama-Nasu R, Pagano M
Nature 2007 Nov 8;450(7167):309-13
Nature 2007 Nov 8;450(7167):309-13
Proteome analysis of proliferative response of bystander cells adjacent to cells exposed to ionizing radiation.
Gerashchenko BI, Yamagata A, Oofusa K, Yoshizato K, de Toledo SM, Howell RW
Proteomics 2007 Jun;7(12):2000-8
Proteomics 2007 Jun;7(12):2000-8
Adeno-associated virus interactions with B23/Nucleophosmin: identification of sub-nucleolar virion regions.
Bevington JM, Needham PG, Verrill KC, Collaco RF, Basrur V, Trempe JP
Virology 2007 Jan 5;357(1):102-13
Virology 2007 Jan 5;357(1):102-13
Global functional analysis of nucleophosmin in Taxol response, cancer, chromatin regulation, and ribosomal DNA transcription.
Bergstralh DT, Conti BJ, Moore CB, Brickey WJ, Taxman DJ, Ting JP
Experimental cell research 2007 Jan 1;313(1):65-76
Experimental cell research 2007 Jan 1;313(1):65-76
SAP30L interacts with members of the Sin3A corepressor complex and targets Sin3A to the nucleolus.
Viiri KM, Korkeamäki H, Kukkonen MK, Nieminen LK, Lindfors K, Peterson P, Mäki M, Kainulainen H, Lohi O
Nucleic acids research 2006;34(11):3288-98
Nucleic acids research 2006;34(11):3288-98
Immunohistochemistry predicts nucleophosmin (NPM) mutations in acute myeloid leukemia.
Falini B, Martelli MP, Bolli N, Bonasso R, Ghia E, Pallotta MT, Diverio D, Nicoletti I, Pacini R, Tabarrini A, Galletti BV, Mannucci R, Roti G, Rosati R, Specchia G, Liso A, Tiacci E, Alcalay M, Luzi L, Volorio S, Bernard L, Guarini A, Amadori S, Mandelli F, Pane F, Lo-Coco F, Saglio G, Pelicci PG, Martelli MF, Mecucci C
Blood 2006 Sep 15;108(6):1999-2005
Blood 2006 Sep 15;108(6):1999-2005
Hepatitis C virus core protein recruits nucleolar phosphoprotein B23 and coactivator p300 to relieve the repression effect of transcriptional factor YY1 on B23 gene expression.
Mai RT, Yeh TS, Kao CF, Sun SK, Huang HH, Wu Lee YH
Oncogene 2006 Jan 19;25(3):448-62
Oncogene 2006 Jan 19;25(3):448-62
Increased levels of the FoxM1 transcription factor accelerate development and progression of prostate carcinomas in both TRAMP and LADY transgenic mice.
Kalin TV, Wang IC, Ackerson TJ, Major ML, Detrisac CJ, Kalinichenko VV, Lyubimov A, Costa RH
Cancer research 2006 Feb 1;66(3):1712-20
Cancer research 2006 Feb 1;66(3):1712-20
Sumoylation induced by the Arf tumor suppressor: a p53-independent function.
Tago K, Chiocca S, Sherr CJ
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2005 May 24;102(21):7689-94
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2005 May 24;102(21):7689-94
Free cholesterol-loaded macrophages are an abundant source of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6: model of NF-kappaB- and map kinase-dependent inflammation in advanced atherosclerosis.
Li Y, Schwabe RF, DeVries-Seimon T, Yao PM, Gerbod-Giannone MC, Tall AR, Davis RJ, Flavell R, Brenner DA, Tabas I
The Journal of biological chemistry 2005 Jun 10;280(23):21763-72
The Journal of biological chemistry 2005 Jun 10;280(23):21763-72
Nucleophosmin (B23) targets ARF to nucleoli and inhibits its function.
Korgaonkar C, Hagen J, Tompkins V, Frazier AA, Allamargot C, Quelle FW, Quelle DE
Molecular and cellular biology 2005 Feb;25(4):1258-71
Molecular and cellular biology 2005 Feb;25(4):1258-71
Proteomic characterization of oxidative dysfunction in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) induced by exposure to oxidized LDL.
Kinumi T, Ogawa Y, Kimata J, Saito Y, Yoshida Y, Niki E
Free radical research 2005 Dec;39(12):1335-44
Free radical research 2005 Dec;39(12):1335-44
Temporal and spatial control of nucleophosmin by the Ran-Crm1 complex in centrosome duplication.
Wang W, Budhu A, Forgues M, Wang XW
Nature cell biology 2005 Aug;7(8):823-30
Nature cell biology 2005 Aug;7(8):823-30
Proteomic analysis reveals hyperactivation of the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway in neurofibromatosis 1-associated human and mouse brain tumors.
Dasgupta B, Yi Y, Chen DY, Weber JD, Gutmann DH
Cancer research 2005 Apr 1;65(7):2755-60
Cancer research 2005 Apr 1;65(7):2755-60
Cyclin G1 has growth inhibitory activity linked to the ARF-Mdm2-p53 and pRb tumor suppressor pathways.
Zhao L, Samuels T, Winckler S, Korgaonkar C, Tompkins V, Horne MC, Quelle DE
Molecular cancer research : MCR 2003 Jan;1(3):195-206
Molecular cancer research : MCR 2003 Jan;1(3):195-206
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Western blot analysis was performed on nuclear enriched cell extracts of K-562 (Lane 1), HCT 116 (Lane 2), HeLa (Lane 3), HEK-293 (Lane 4), Neuro-2a (Lane 5), NTERA-2 cl.D1 (Lane 6), SH-SY5Y (lane 7), PC-12 (lane 8) and NIH/3T3 (Lane 9). Blots were probed with Anti- Nucleophosmin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (Product # 32-5200, 2 µg/mL) and detected by chemiluminescence using Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Superclonal™ Secondary Antibody, HRP conj µgate (Product # A28177, 0.4 µg/mL, 1:2500 dilution). A ~ 37 kDa band corresponding to Nucleophosmin was observed across all cell lines. An additional ~ 33 kDa band corresponding to Nucleophosmin isoform was observed in HCT 116 (Lane 2), HEK-293 (Lane 4), Neuro-2a (Lane 5), NTERA-2 cl.D1 (Lane 6) and SH-SY5Y (lane 7). Bands of ~210 kDa observed in K-562 (Lane 1), HeLa (Lane 3) and PC-12 (lane 8) could be due to oligomerisation of Nucleophosmin. Protein samples were electrophoresed using Novex® NuPAGE® 4-12 % Bis-Tris gel (Product # NP0321BOX), XCell SureLock™ Electrophoresis System (Product # EI0002) and Novex® Sharp Pre-Stained Protein Standard (Product # LC5800). Resolved proteins were transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane and probed with the relevant primary and secondary Antibody following blocking with 5 % skimmed milk. Chemiluminescent detection was performed using Pierce™ ECL Western Blotting Substrate (Product # 32106).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Knockdown of NPM1 was achieved by transfecting HeLa with NPM1 specific siRNAs (Silencer® select Product # s9677, s9676). Western blot analysis (Fig. a) was performed using modified whole cell extracts (1% SDS) from the NPM1 knockdown cells (Lane 3), non-specific scrambled siRNA transfected cells (Lane 2) and untransfected cells (Lane 1). The blot was probed with NPM1 Monoclonal Antibody (FC-61991) (Product # 32-5200, 0.5 ug/mL) and Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L), Superclonal™ Recombinant Secondary Antibody, HRP (Product # A27036, 1:4000 dilution). Densitometric analysis of this western blot for the 36 kDa band is shown in Fig. b and for the 230 kDa band in Fig. c. Decrease in signal upon siRNA mediated knock down confirms that antibody is specific to NPM1.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of Nucleophosmin was performed using 70% confluent log phase A549 cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton™ X-100 for 10 minutes, and blocked with 1% BSA for 1 hour at room temperature. The cells were labeled with Nucleophosmin (FC-61991) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (Product # 32-5200) at 2 µg/mL in 0.1% BSA and incubated for 3 hours at room temperature and then labeled with Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Superclonal™ Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conj µgate (Product # A28175) at a dilution of 1:2000 for 45 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: green). Nuclei (Panel b: blue) were stained with SlowFade® Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938). F-actin (Panel c: red) was stained with Alexa Fluor® 555 Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300). Panel d represents the merged image showing nucleolar localization. Panel e shows the no primary antibody control. The images were captured at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of Nucleophosmin (green) in HeLa cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS for 15 minutes, and blocked with 3% Blocker BSA (Product # 37525) in PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were stained with a Nucleophosmin monoclonal antibody (Product # 32-5200) at a concentration of 10 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature, and then incubated with a Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Superclonal Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 conjugate (Product # A28175) at a dilution of 1:1000 for 1 hour at room temperature (green). Nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst 33342 dye (Product # 62249). Images were taken on a Thermo Scientific ToxInsight at 20X magnification.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemical staining of human colon cancer tissue using Mouse anti-Nucleophosmin monoclonal antibody (clone FC-61991) (Product # 32-5200).
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of Nucleophosmin was done on A549 cells. Cells were fixed with 70% ethanol for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.25% Triton™ X-100 for 20 minutes, and blocked with 5% BSA for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were labeled with Nucleophosmin Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (Product # 32-5200, red histogram) or with mouse isotype control (pink histogram) at 3-5 µg/million cells in 2.5% BSA. After incubation at room temperature for 2 hours, the cells were labeled with Alexa Fluor® 488 Rabbit Anti-Mouse Secondary Antibody (Product # A11059) at a dilution of 1:400 for 30 minutes at room temperature. The representative 10, 000 cells were acquired and analyzed for each sample using an Attune® Acoustic Focusing Cytometer. The purple histogram represents unstained control cells and the green histogram represents no-primary-antibody control.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
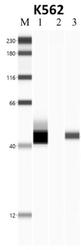
- Experimental details
- Immunoprecipitation of NPM1 was performed on K562 cells. Antigen-antibody complexes were formed by incubating approximately 500 µg whole cell lysate with 5 µg of NPM1 monoclonal antibody (Product # 325200) rotating 60 min at RT. The immune complexes were captured on 625 µg of anti-mouse coated Dynabeads (Product # 11202D) and washed extensively. They were then eluted and analyzed using the Jess Simple Western system. Lane 1 is input, lane 2 IP without antibody and lane 3 IP with antibody. Target was detected a NPM1 monoclonal antibody (Product # 325200) at a dilution of 1:25, followed by a 1:100 dilution of secondary antibody. Data courtesy of the Yeo lab as part of the ENCODE project (www.encodeproject.org).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
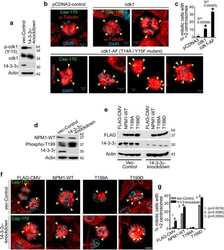
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
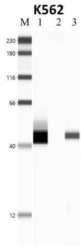
- Experimental details
- RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) western of NPM1 was performed on K562 cells. Antigen-antibody complexes were formed by incubating approximately 500 µg whole cell lysate with 5 µg of NPM1 monoclonal antibody (Product # 325200) rotating 60 min at RT. The immune complexes were captured on 625 µg of anti-mouse coated Dynabeads (Product # 11202D) and washed extensively. They were then eluted and analyzed using the Jess Simple Western system. Lane 1 is input, lane 2 IP without antibody and lane 3 IP with antibody. Target was detected a NPM1 monoclonal antibody (Product # 325200) at a dilution of 1:25, followed by a 1:100 dilution of secondary antibody. Data courtesy of the Yeo lab as part of the ENCODE project (www.encodeproject.org).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

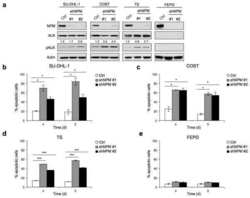
- Experimental details
- Figure 5 P-STAT5 regulates p53/MDM2 functions and cell survival through NPM1 protein. ( a ) HEK 293T cells (6 x 10 5 per well) transfected with either RFP-STAT5A or RFP-backbone vectors were harvested at 24 h after transfection, and the cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting assays for detection of expression levels of p53 and its phosphorylation levels at serine 15 and threonine 18, as well as the expression levels of MDM2 and its phosphorylation level at serine 166. ( b ) Six hours after transfection with either RFP-STAT5A or RFP-backbone vectors, HEK 293T cells (6 x 10 5 per well) were incubated overnight with inhibitor 573108 at a concentration of 340 mu M and then harvested and lysed for immunoblotting assays to examine the expression levels of p53 and MDM2 as well as their relevant phosphorylation levels. ( c and d ) HEK 293T cells (6 x 10 5 per well) were transfected with RFP-STAT5AY694F mutant vector for 24 h, harvested and lysed for immunoblotting assays on the expression levels of MDM2, p53 and p21. ( e ) HEK 293T cells (6 x 10 5 per well) were co-transfected with RFP-wtSTAT5A and FLAG-NPM1 vectors for 24 h, harvested and lysed for immunoblotting assays on the p53 expression levels. ( f ) MCF-7 cells (2 x 10 6 per well) were plated on 10 cm plate on day 0 and then lentivirally transduced with pLVX-IRES-mCherry-wtSTAT5 or pLVX-IRES-mCherry-STAT5Y694F on day 1. The cells were harvested 72 h after the transduction and lysed for immunoblotting assays. ( g ) HEK 2
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) western of NPM1 was performed on K562 cells. Antigen-antibody complexes were formed by incubating approximately 500 µg whole cell lysate with 5 µg of NPM1 monoclonal antibody (Product # 325200) rotating 60 min at RT. The immune complexes were captured on 625 µg of anti-mouse coated Dynabeads (Product # 11202D) and washed extensively. They were then eluted and analyzed using the Jess Simple Western system. Lane 1 is input, lane 2 IP without antibody and lane 3 IP with antibody. Target was detected a NPM1 monoclonal antibody (Product # 325200) at a dilution of 1:25, followed by a 1:100 dilution of secondary antibody. Data courtesy of the Yeo lab as part of the ENCODE project (www.encodeproject.org).
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn