12-1529-42
antibody from Invitrogen Antibodies
Targeting: CTLA4
CD, CD152, CELIAC3, CTLA-4, GSE, IDDM12
Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [31]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Flow cytometry [1]
- Other assay [8]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 12-1529-42 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- CD152 (CTLA-4) Monoclonal Antibody (14D3), PE, eBioscience™
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Other
- Description
- Description: The 14D3 monoclonal antibody reacts with human CD152, also known as cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4). CTLA-4, a protein with structural similarities to CD28, is expressed on activated T cells (activated B cells may also express CTLA-4) and binds the B7 family members, CD80 (B7-1) and CD86 (B7-2), with higher affinity than CD28 does. CTLA-4 and CD28 appear to deliver opposing signals to T cells: while CD28 is a potent costimulator, CTLA-4 restricts the progression of T cells to an activated state by inhibiting IL-2 secretion and cellular proliferation. The cytoplasmic portion of CTLA-4 contains ER retention motifs, resulting in intracellular localization of a large proportion of newly synthesized CTLA-4 in response to TCR signaling. The 14D3 antibody also recognizes rhesus monkey and has inhibitor activity. Applications Reported: The 14D3 antibody has been reported for use in flow cytometric analysis. Applications Tested: This 14D3 antibody has been pre-titrated and tested by intracellular staining and flow cytometric analysis of stimulated human peripheral blood cells using the Intracellular Fixation & Permeabilization Buffer Set (Product # 88-8824-00) and protocol. Please refer to Best Protocols: Protocol A: Two step protocol for (cytoplasmic) intracellular proteins located under the Resources Tab online. This can be used at 5 µL (0.03 µg) per test. A test is defined as the amount (µg) of antibody that will stain a cell sample in a final volume of 100 µL. Cell number should be determined empirically but can range from 10^5 to 10^8 cells/test. Furthermore, due to the intracellular localization of a large portion of CTLA-4, for complete detection it may be necessary to assess intracellular expression, in addition to surface expression of CTLA-4. Excitation: 488-561 nm; Emission: 578 nm; Laser: Blue Laser, Green Laser, Yellow-Green Laser. Filtration: 0.2 µm post-manufacturing filtered.
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Mouse
- Conjugate
- Yellow dye
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- 14D3
- Vial size
- 100 Tests
- Concentration
- 5 µL/Test
- Storage
- 4° C, store in dark, DO NOT FREEZE!
Submitted references Immunometabolic analysis shows a distinct cyto-metabotype in Covid-19 compared to sepsis from other causes.
Mesenchymal stem cells transfer mitochondria to allogeneic Tregs in an HLA-dependent manner improving their immunosuppressive activity.
Cancer stem-like cells evade CD8(+)CD103(+) tumor-resident memory T (T(RM)) lymphocytes by initiating an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition program in a human lung tumor model.
Engineering advanced logic and distributed computing in human CAR immune cells.
Developing Human Skin Contains Lymphocytes Demonstrating a Memory Signature.
Methylome-based cell-of-origin modeling (Methyl-COOM) identifies aberrant expression of immune regulatory molecules in CLL.
Accumulation of TNFR2-expressing regulatory T cells in malignant pleural effusion of lung cancer patients is associated with poor prognosis.
Schistosoma mansoni rSm29 Antigen Induces a Regulatory Phenotype on Dendritic Cells and Lymphocytes From Patients With Cutaneous Leishmaniasis.
Functionalization-dependent effects of cellulose nanofibrils on tolerogenic mechanisms of human dendritic cells.
Hepatocyte-derived exosomes promote T follicular regulatory cell expansion during hepatitis C virus infection.
Turning the tables on cytomegalovirus: targeting viral Fc receptors by CARs containing mutated CH2-CH3 IgG spacer domains.
Azacytidine prevents experimental xenogeneic graft-versus-host disease without abrogating graft-versus-leukemia effects.
Functional characterization of T-cells from palatine tonsils in patients with chronic tonsillitis.
Toll-like receptor 2 induced cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 regulates Aspergillus-induced regulatory T-cells with pro-inflammatory characteristics.
Mitochondrial dysregulation and glycolytic insufficiency functionally impair CD8 T cells infiltrating human renal cell carcinoma.
Chronic Critical Illness from Sepsis Is Associated with an Enhanced TCR Response.
HDAC inhibition potentiates immunotherapy in triple negative breast cancer.
Vaccination with High-Affinity Epitopes Impairs Antitumor Efficacy by Increasing PD-1 Expression on CD8(+) T Cells.
Impact of immunosuppressive drugs on the therapeutic efficacy of ex vivo expanded human regulatory T cells.
Statins increase the frequency of circulating CD4+ FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in healthy individuals.
Follicular regulatory T cells impair follicular T helper cells in HIV and SIV infection.
The immunosuppressive enzyme IL4I1 promotes FoxP3(+) regulatory T lymphocyte differentiation.
Effect of chorioamnionitis on regulatory T cells in moderate/late preterm neonates.
Progression of Lung Cancer Is Associated with Increased Dysfunction of T Cells Defined by Coexpression of Multiple Inhibitory Receptors.
Synovial Regulatory T Cells Occupy a Discrete TCR Niche in Human Arthritis and Require Local Signals To Stabilize FOXP3 Protein Expression.
Hypomethylation at the regulatory T cell-specific demethylated region in CD25hi T cells is decoupled from FOXP3 expression at the inflamed site in childhood arthritis.
Circulating T regulatory cells migration and phenotype in glioblastoma patients: an in vitro study.
Bet v 1-specific T-cell receptor/forkhead box protein 3 transgenic T cells suppress Bet v 1-specific T-cell effector function in an activation-dependent manner.
The effects of trastuzumab on the CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ and CD4+IL17A+ T-cell axis in patients with breast cancer.
Soluble CTLA-4 in autoimmune thyroid diseases: relationship with clinical status and possible role in the immune response dysregulation.
Renal allograft rejection is prevented by adoptive transfer of anergic T cells in nonhuman primates.
Trovato FM, Mujib S, Jerome E, Cavazza A, Morgan P, Smith J, Depante MT, O'Reilly K, Luxton J, Mare T, Napoli S, McPhail MJ
Heliyon 2022 Jun;8(6):e09733
Heliyon 2022 Jun;8(6):e09733
Mesenchymal stem cells transfer mitochondria to allogeneic Tregs in an HLA-dependent manner improving their immunosuppressive activity.
Piekarska K, Urban-Wójciuk Z, Kurkowiak M, Pelikant-Małecka I, Schumacher A, Sakowska J, Spodnik JH, Arcimowicz Ł, Zielińska H, Tymoniuk B, Renkielska A, Siebert J, Słomińska E, Trzonkowski P, Hupp T, Marek-Trzonkowska NM
Nature communications 2022 Feb 14;13(1):856
Nature communications 2022 Feb 14;13(1):856
Cancer stem-like cells evade CD8(+)CD103(+) tumor-resident memory T (T(RM)) lymphocytes by initiating an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition program in a human lung tumor model.
Corgnac S, Damei I, Gros G, Caidi A, Terry S, Chouaib S, Deloger M, Mami-Chouaib F
Journal for immunotherapy of cancer 2022 Apr;10(4)
Journal for immunotherapy of cancer 2022 Apr;10(4)
Engineering advanced logic and distributed computing in human CAR immune cells.
Cho JH, Okuma A, Sofjan K, Lee S, Collins JJ, Wong WW
Nature communications 2021 Feb 4;12(1):792
Nature communications 2021 Feb 4;12(1):792
Developing Human Skin Contains Lymphocytes Demonstrating a Memory Signature.
Dhariwala MO, Karthikeyan D, Vasquez KS, Farhat S, Weckel A, Taravati K, Leitner EG, Clancy S, Pauli M, Piper ML, Cohen JN, Ashouri JF, Lowe MM, Rosenblum MD, Scharschmidt TC
Cell reports. Medicine 2020 Nov 17;1(8):100132
Cell reports. Medicine 2020 Nov 17;1(8):100132
Methylome-based cell-of-origin modeling (Methyl-COOM) identifies aberrant expression of immune regulatory molecules in CLL.
Wierzbinska JA, Toth R, Ishaque N, Rippe K, Mallm JP, Klett LC, Mertens D, Zenz T, Hielscher T, Seifert M, Küppers R, Assenov Y, Lutsik P, Stilgenbauer S, Roessner PM, Seiffert M, Byrd J, Oakes CC, Plass C, Lipka DB
Genome medicine 2020 Mar 18;12(1):29
Genome medicine 2020 Mar 18;12(1):29
Accumulation of TNFR2-expressing regulatory T cells in malignant pleural effusion of lung cancer patients is associated with poor prognosis.
Ye LL, Peng WB, Niu YR, Xiang X, Wei XS, Wang ZH, Wang X, Zhang SY, Chen X, Zhou Q
Annals of translational medicine 2020 Dec;8(24):1647
Annals of translational medicine 2020 Dec;8(24):1647
Schistosoma mansoni rSm29 Antigen Induces a Regulatory Phenotype on Dendritic Cells and Lymphocytes From Patients With Cutaneous Leishmaniasis.
Lopes DM, Oliveira SC, Page B, Carvalho LP, Carvalho EM, Cardoso LS
Frontiers in immunology 2018;9:3122
Frontiers in immunology 2018;9:3122
Functionalization-dependent effects of cellulose nanofibrils on tolerogenic mechanisms of human dendritic cells.
Tomić S, Ilić N, Kokol V, Gruden-Movsesijan A, Mihajlović D, Bekić M, Sofronić-Milosavljević L, Čolić M, Vučević D
International journal of nanomedicine 2018;13:6941-6960
International journal of nanomedicine 2018;13:6941-6960
Hepatocyte-derived exosomes promote T follicular regulatory cell expansion during hepatitis C virus infection.
Cobb DA, Kim OK, Golden-Mason L, Rosen HR, Hahn YS
Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2018 Jan;67(1):71-85
Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2018 Jan;67(1):71-85
Turning the tables on cytomegalovirus: targeting viral Fc receptors by CARs containing mutated CH2-CH3 IgG spacer domains.
Proff J, Brey CU, Ensser A, Holter W, Lehner M
Journal of translational medicine 2018 Feb 8;16(1):26
Journal of translational medicine 2018 Feb 8;16(1):26
Azacytidine prevents experimental xenogeneic graft-versus-host disease without abrogating graft-versus-leukemia effects.
Ehx G, Fransolet G, de Leval L, D'Hondt S, Lucas S, Hannon M, Delens L, Dubois S, Drion P, Beguin Y, Humblet-Baron S, Baron F
Oncoimmunology 2017;6(5):e1314425
Oncoimmunology 2017;6(5):e1314425
Functional characterization of T-cells from palatine tonsils in patients with chronic tonsillitis.
Geißler K, Markwart R, Requardt RP, Weigel C, Schubert K, Scherag A, Rubio I, Guntinas-Lichius O
PloS one 2017;12(9):e0183214
PloS one 2017;12(9):e0183214
Toll-like receptor 2 induced cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 regulates Aspergillus-induced regulatory T-cells with pro-inflammatory characteristics.
Raijmakers RPH, Sprenkeler EGG, Aleva FE, Jacobs CWM, Kanneganti TD, Joosten LAB, van de Veerdonk FL, Gresnigt MS
Scientific reports 2017 Sep 13;7(1):11500
Scientific reports 2017 Sep 13;7(1):11500
Mitochondrial dysregulation and glycolytic insufficiency functionally impair CD8 T cells infiltrating human renal cell carcinoma.
Siska PJ, Beckermann KE, Mason FM, Andrejeva G, Greenplate AR, Sendor AB, Chiang YJ, Corona AL, Gemta LF, Vincent BG, Wang RC, Kim B, Hong J, Chen CL, Bullock TN, Irish JM, Rathmell WK, Rathmell JC
JCI insight 2017 Jun 15;2(12)
JCI insight 2017 Jun 15;2(12)
Chronic Critical Illness from Sepsis Is Associated with an Enhanced TCR Response.
Borken F, Markwart R, Requardt RP, Schubert K, Spacek M, Verner M, Rückriem S, Scherag A, Oehmichen F, Brunkhorst FM, Rubio I
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2017 Jun 15;198(12):4781-4791
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2017 Jun 15;198(12):4781-4791
HDAC inhibition potentiates immunotherapy in triple negative breast cancer.
Terranova-Barberio M, Thomas S, Ali N, Pawlowska N, Park J, Krings G, Rosenblum MD, Budillon A, Munster PN
Oncotarget 2017 Dec 26;8(69):114156-114172
Oncotarget 2017 Dec 26;8(69):114156-114172
Vaccination with High-Affinity Epitopes Impairs Antitumor Efficacy by Increasing PD-1 Expression on CD8(+) T Cells.
Zahm CD, Colluru VT, McNeel DG
Cancer immunology research 2017 Aug;5(8):630-641
Cancer immunology research 2017 Aug;5(8):630-641
Impact of immunosuppressive drugs on the therapeutic efficacy of ex vivo expanded human regulatory T cells.
Scottà C, Fanelli G, Hoong SJ, Romano M, Lamperti EN, Sukthankar M, Guggino G, Fazekasova H, Ratnasothy K, Becker PD, Afzali B, Lechler RI, Lombardi G
Haematologica 2016 Jan;101(1):91-100
Haematologica 2016 Jan;101(1):91-100
Statins increase the frequency of circulating CD4+ FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in healthy individuals.
Rodríguez-Perea AL, Montoya CJ, Olek S, Chougnet CA, Velilla PA
Journal of immunology research 2015;2015:762506
Journal of immunology research 2015;2015:762506
Follicular regulatory T cells impair follicular T helper cells in HIV and SIV infection.
Miles B, Miller SM, Folkvord JM, Kimball A, Chamanian M, Meditz AL, Arends T, McCarter MD, Levy DN, Rakasz EG, Skinner PJ, Connick E
Nature communications 2015 Oct 20;6:8608
Nature communications 2015 Oct 20;6:8608
The immunosuppressive enzyme IL4I1 promotes FoxP3(+) regulatory T lymphocyte differentiation.
Cousin C, Aubatin A, Le Gouvello S, Apetoh L, Castellano F, Molinier-Frenkel V
European journal of immunology 2015 Jun;45(6):1772-82
European journal of immunology 2015 Jun;45(6):1772-82
Effect of chorioamnionitis on regulatory T cells in moderate/late preterm neonates.
Rueda CM, Wells CB, Gisslen T, Jobe AH, Kallapur SG, Chougnet CA
Human immunology 2015 Jan;76(1):65-73
Human immunology 2015 Jan;76(1):65-73
Progression of Lung Cancer Is Associated with Increased Dysfunction of T Cells Defined by Coexpression of Multiple Inhibitory Receptors.
Thommen DS, Schreiner J, Müller P, Herzig P, Roller A, Belousov A, Umana P, Pisa P, Klein C, Bacac M, Fischer OS, Moersig W, Savic Prince S, Levitsky V, Karanikas V, Lardinois D, Zippelius A
Cancer immunology research 2015 Dec;3(12):1344-55
Cancer immunology research 2015 Dec;3(12):1344-55
Synovial Regulatory T Cells Occupy a Discrete TCR Niche in Human Arthritis and Require Local Signals To Stabilize FOXP3 Protein Expression.
Bending D, Giannakopoulou E, Lom H, Wedderburn LR
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2015 Dec 15;195(12):5616-24
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2015 Dec 15;195(12):5616-24
Hypomethylation at the regulatory T cell-specific demethylated region in CD25hi T cells is decoupled from FOXP3 expression at the inflamed site in childhood arthritis.
Bending D, Pesenacker AM, Ursu S, Wu Q, Lom H, Thirugnanabalan B, Wedderburn LR
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2014 Sep 15;193(6):2699-708
Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md. : 1950) 2014 Sep 15;193(6):2699-708
Circulating T regulatory cells migration and phenotype in glioblastoma patients: an in vitro study.
Vasco C, Canazza A, Rizzo A, Mossa A, Corsini E, Silvani A, Fariselli L, Salmaggi A, Ciusani E
Journal of neuro-oncology 2013 Dec;115(3):353-63
Journal of neuro-oncology 2013 Dec;115(3):353-63
Bet v 1-specific T-cell receptor/forkhead box protein 3 transgenic T cells suppress Bet v 1-specific T-cell effector function in an activation-dependent manner.
Schmetterer KG, Haiderer D, Leb-Reichl VM, Neunkirchner A, Jahn-Schmid B, Küng HJ, Schuch K, Steinberger P, Bohle B, Pickl WF
The Journal of allergy and clinical immunology 2011 Jan;127(1):238-45, 245.e1-3
The Journal of allergy and clinical immunology 2011 Jan;127(1):238-45, 245.e1-3
The effects of trastuzumab on the CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ and CD4+IL17A+ T-cell axis in patients with breast cancer.
Horlock C, Stott B, Dyson PJ, Morishita M, Coombes RC, Savage P, Stebbing J
British journal of cancer 2009 Apr 7;100(7):1061-7
British journal of cancer 2009 Apr 7;100(7):1061-7
Soluble CTLA-4 in autoimmune thyroid diseases: relationship with clinical status and possible role in the immune response dysregulation.
Saverino D, Brizzolara R, Simone R, Chiappori A, Milintenda-Floriani F, Pesce G, Bagnasco M
Clinical immunology (Orlando, Fla.) 2007 May;123(2):190-8
Clinical immunology (Orlando, Fla.) 2007 May;123(2):190-8
Renal allograft rejection is prevented by adoptive transfer of anergic T cells in nonhuman primates.
Bashuda H, Kimikawa M, Seino K, Kato Y, Ono F, Shimizu A, Yagita H, Teraoka S, Okumura K
The Journal of clinical investigation 2005 Jul;115(7):1896-902
The Journal of clinical investigation 2005 Jul;115(7):1896-902
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
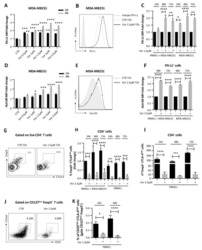
- PHA-stimulated human peripheral blood cells were intracellularly stained with Mouse IgG2a K Isotype Control PE (Product # 12-4724-81) (blue histogram) or Anti-Human CD152 (CTLA-4) PE (purple histogram) using the Intracellular Fixation & Permeabilization Buffer Set (Product # 88-8824-00) and protocol. Cells in the lymphocyte gate were used for analysis.
- Conjugate
- Yellow dye
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Conjugate
- Yellow dye
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- NULL
- Conjugate
- Yellow dye
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Figure 6 T FR exhibit an enhanced regulatory phenotype in ex vivo HIV infection. Tonsil cells were mock-, X4-, or R5-spinoculated and cultured under experimental conditions as indicated. T FR were then analysed for expression of regulatory receptors and cytokine production by intracellular cytokine staining. ( a ) Percentage of total (surface and intracellular) T FR CTLA-4 expression ( n =15). ( b ) Percentage of surface T FR LAG-3 expression ( n =8). ( c ) Production of IL-10 by T FR ( n =7). ( d ) Production of TGF-beta-1 (measured as LAP) by T FR ( n =5). The horizontal bars of each graph indicate the median value and are listed where appropriate for clarity. Statistical analyses were performed by Friedman ( a , b ) or Mann-Whitney tests ( c , d ) and significance is denoted by asterisks where * P
- Conjugate
- Yellow dye
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Resident memory T (T RM ) and non-T RM phenotypic profiles and susceptibility of cancer stem cell (CSC) to cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL)-mediated killing. (A) Flow cytometry analyses of CD8, LFA-1, CD103, CD49a, CD69, PD-1, CTLA-4, TGFBR2 and VEGFR2 on CD8 + CD103 + T RM (Heu171) and CD8 + CD103 - non-T RM (H32-22) clones. Mean immunofluorescence intensity (MFI) are in parentheses. (B) Cytotoxic activity of the T RM clone (Heu171) towards autologous IGR-Heu, Heu-CSC, CSC-1 and CSC-2 target cells. Percent of specific lysis are shown at indicated effector to target (E:T) ratios. (C) Quantification of transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta in conditioned media from IGR-Heu, Heu-CSC, CSC-1 and CSC-2 by multi-analyte flow assay. Ratios of active/total TGF-beta normalized to IGR-Heu are included. Results are presented as mean+-SEM of duplicates. (D) Cytotoxicity of the non-T RM clone (H32-22) towards autologous IGR-Heu, Heu-CSC, CSC-1 and CSC-2 target cells. (E) Inhibition of T RM -cell-mediated killing. CSC-1 cells are preincubated in the presence of isotype control, anti-major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) or anti-intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) neutralizing monoclonal antibody (mAb) and then CTL were added at 5:1 E:T ratio. Symbols represent replicates and horizontal bars represent means+-SEM (n=3). P value was determined by two-way analysis of variance test. *p
- Conjugate
- Yellow dye
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Effects of TNF on the suppressive function of TNFR2 + Tregs. Purified CD4 + T cells were cultured in medium alone, TNF (50 ng/mL), TNF combined with anti-TNFR2 mAbs (10 ug/mL), or isotype IgG, as indicated, for 72 hours. The representative FACS analysis of (A) CTLA-4 + cells and (B) PD-L1 + cells in TNFR2 + Tregs as indicated, gated on live CD4 + Foxp3 + cells. Summary of the proportions of (C) CTLA-4 + cells (n=3) and (D) PD-L1 + cells (n=3) in Tregs within each condition. Data are expressed as means +- SEM. *, P
- Conjugate
- Yellow dye
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Figure 2 T FR expansion in lymphoid tissues during chronic SIV infection. ( a ) Disaggregated lymph node and spleen cells from SIV uninfected ( n =9) or chronically SIV-infected rhesus macaques ( n =11) were analysed by flow cytometry. Representative examples of flow cytometry gating are shown. Of viable CD3 + CD8 - cells, follicular subsets were defined as CXCR5 + cells (F) and germinal centre subsets were defined as CXCR5 hi PD-1 hi cells (GC). Of these subsets, regulatory cells were defined as CD25 hi CD127 - . T FR (CXCR5 + CD25 hi CD127 - ) were Foxp3 + , whereas T FH (CXCR5 + CD25 lo/- ) were Foxp3 - . ( b ) The percentages of each rhesus macaque regulatory subset, as analysed in a are shown. ( c ) The ratios of each regulatory cell population to its non-regulatory cell counterpart are shown. ( d ) The percentage of total CTLA-4 expression is shown in SIV-uninfected ( n =9) and chronically SIV-infected ( n =8) rhesus macaques. The horizontal bars of each graph indicate the median value and are listed where appropriate for clarity. Statistical analyses were performed by Mann-Whitney (Wilcoxon) tests to compare unpaired, nonparametric values and significance is denoted by asterisks where * P
- Conjugate
- Yellow dye
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
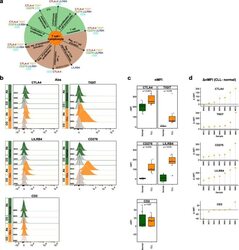
- Fig. 6 Flow cytometry analysis of T cell-/lymphocyte-specific markers on normal and malignant B cells from CLL patients. a Summary scheme representing functional implications of CLL-specific candidate genes selected for flow cytometric analysis. b Flow cytometric analysis of expression of CTLA-4, TIGIT, CD276, LILRB4, and CD2 on peripheral blood B cells of CLL patients. The expression was determined for non-malignant B cells (""Normal""; CD19 + CD5 - B cells, represented in green) and neoplastic B cells (""CLL"", CD19 + CD5 + B cells, represented in orange) detected in the same samples. ""Co,"" no antibody staining control; ""Ab,"" staining with the antibody of interest as indicated. c Normalized median fluorescence intensities (target MFI - MFI of negative control [Co]; nMFI). d Delta normalized median fluorescence intensities between CLL cells and normal B cells (DeltanMFI (CLL-normal)) for each patient tested
- Conjugate
- Yellow dye
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Fig. 3 The intracellular AND logic with different signaling domains. a Diagram of intracellular AND logic. b Primary human CD8+ T cells were transduced with FOS zipCAR-containing CD3zeta domain and RR zipCAR-containing CD28 domain. Cytotoxicity against Her2- and Axl-expressing Nalm6 was measured 24 h after adding alpha-Her2-SYN9 and/or alpha-Axl-EE zipFvs. The heatmap indicates cytotoxicity at varying zipFv concentrations ( n = 3, data are represented as mean). c Cytotoxicity of CD8+ T cells transduced with FOS zipCAR-containing CD3zeta domain and RR zipCAR-containing 4-1BB domain. The heatmap indicates cytotoxicity at varying zipFv concentrations ( n = 3, data are represented as mean). d (Left) Isolated Treg cells were transduced with two zipCAR constructs: SYN6-CD3zeta-P2A-FOXP3 and SYN1-CD28-P2A-puro. After puromycin selection (2 mug/mL), Treg cells were co-cultured with Her2- and Axl-expressing Nalm6 target cells (Right) The heatmap shows surface CTLA-4 expression detected after 48 h by flow cytometry at varying zipFv concentrations (alpha-Axl-SYN5 and alpha-Her2-SYN2) ( n = 3, data are represented as mean).
- Conjugate
- Yellow dye
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry