Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [8]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Western blot [1]
- Immunohistochemistry [2]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 20392-1-AP - Provider product page

- Provider
- Proteintech Group
- Proper citation
- Proteintech Cat#20392-1-AP, RRID:AB_10693618
- Product name
- STAC3 antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Description
- KD/KO validated STAC3 antibody (Cat. #20392-1-AP) is a rabbit polyclonal antibody that shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat and has been validated for the following applications: IHC, WB, ELISA.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Host
- Rabbit
- Conjugate
- Unconjugated
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 20ul, 150ul
Submitted references Intrinsic contractile dysfunction due to impaired sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) release in compensatory hypertrophied muscle fibers following synergist ablation.
Calcium current modulation by the γ1 subunit depends on alternative splicing of CaV1.1.
Dissociation of SH3 and cysteine-rich domain 3 and junctophilin 1 from dihydropyridine receptor in dystrophin-deficient muscles.
Preconditioning contractions prevent prolonged force depression and Ca(2+)-dependent proteolysis of STAC3 after damaging eccentric contractions.
Multiple Sequence Variants in STAC3 Affect Interactions with Ca(V)1.1 and Excitation-Contraction Coupling.
STAC3 variants cause a congenital myopathy with distinctive dysmorphic features and malignant hyperthermia susceptibility.
STAC3 incorporation into skeletal muscle triads occurs independent of the dihydropyridine receptor.
The SH3 and cysteine-rich domain 3 (Stac3) gene is important to growth, fiber composition, and calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in postnatal skeletal muscle.
Tokuda N, Watanabe D, Naito A, Yamauchi N, Ashida Y, Cheng AJ, Yamada T
American journal of physiology. Cell physiology 2023 Sep 1;325(3):C599-C612
American journal of physiology. Cell physiology 2023 Sep 1;325(3):C599-C612
Calcium current modulation by the γ1 subunit depends on alternative splicing of CaV1.1.
El Ghaleb Y, Ortner NJ, Posch W, Fernández-Quintero ML, Tuinte WE, Monteleone S, Draheim HJ, Liedl KR, Wilflingseder D, Striessnig J, Tuluc P, Flucher BE, Campiglio M
The Journal of general physiology 2022 Sep 5;154(9)
The Journal of general physiology 2022 Sep 5;154(9)
Dissociation of SH3 and cysteine-rich domain 3 and junctophilin 1 from dihydropyridine receptor in dystrophin-deficient muscles.
Ashida Y, Himori K, Tokuda N, Naito A, Yamauchi N, Takenaka-Ninagawa N, Aoki Y, Sakurai H, Yamada T
American journal of physiology. Cell physiology 2022 Sep 1;323(3):C885-C895
American journal of physiology. Cell physiology 2022 Sep 1;323(3):C885-C895
Preconditioning contractions prevent prolonged force depression and Ca(2+)-dependent proteolysis of STAC3 after damaging eccentric contractions.
Ashida Y, Himori K, Tamai K, Kimura I, Yamada T
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2021 Nov 1;131(5):1399-1407
Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 2021 Nov 1;131(5):1399-1407
Multiple Sequence Variants in STAC3 Affect Interactions with Ca(V)1.1 and Excitation-Contraction Coupling.
Rufenach B, Christy D, Flucher BE, Bui JM, Gsponer J, Campiglio M, Van Petegem F
Structure (London, England : 1993) 2020 Aug 4;28(8):922-932.e5
Structure (London, England : 1993) 2020 Aug 4;28(8):922-932.e5
STAC3 variants cause a congenital myopathy with distinctive dysmorphic features and malignant hyperthermia susceptibility.
Zaharieva IT, Sarkozy A, Munot P, Manzur A, O'Grady G, Rendu J, Malfatti E, Amthor H, Servais L, Urtizberea JA, Neto OA, Zanoteli E, Donkervoort S, Taylor J, Dixon J, Poke G, Foley AR, Holmes C, Williams G, Holder M, Yum S, Medne L, Quijano-Roy S, Romero NB, Fauré J, Feng L, Bastaki L, Davis MR, Phadke R, Sewry CA, Bönnemann CG, Jungbluth H, Bachmann C, Treves S, Muntoni F
Human mutation 2018 Dec;39(12):1980-1994
Human mutation 2018 Dec;39(12):1980-1994
STAC3 incorporation into skeletal muscle triads occurs independent of the dihydropyridine receptor.
Campiglio M, Kaplan MM, Flucher BE
Journal of cellular physiology 2018 Dec;233(12):9045-9051
Journal of cellular physiology 2018 Dec;233(12):9045-9051
The SH3 and cysteine-rich domain 3 (Stac3) gene is important to growth, fiber composition, and calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum in postnatal skeletal muscle.
Cong X, Doering J, Mazala DA, Chin ER, Grange RW, Jiang H
Skeletal muscle 2016;6:17
Skeletal muscle 2016;6:17
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Proteintech Group (provider)
- Main image
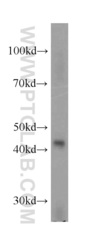
- Experimental details
- human testis tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with 20392-1-AP(STAC3 antibody) at dilution of 1:300
- Sample type
- tissue
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Proteintech Group (provider)
- Main image
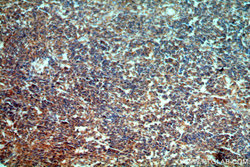
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemical of paraffin-embedded human gliomas using 20392-1-AP(STAC3 antibody) at dilution of 1:50 (under 10x lens)
- Sample type
- tissue
- Submitted by
- Proteintech Group (provider)
- Main image
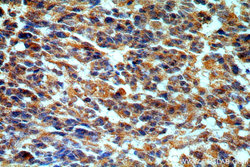
- Experimental details
- The STAC3 antibody from Proteintech is a rabbit polyclonal antibody to a fusion protein of human STAC3. This antibody recognizes human, mouse, rat antigen. The STAC3 antibody has been validated for the following applications: ELISA, WB, IHC analysis.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot ELISA
ELISA