Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [12]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Western blot [2]
- Immunohistochemistry [2]
- Other assay [1]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- NBP1-05197 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Novus Biologicals
- Proper citation
- Novus Cat#NBP1-05197, RRID:AB_1555288
- Product name
- Mouse Monoclonal GFAP Antibody
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Description
- Immunogen affinity purified.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Porcine
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Vial size
- 0.1 ml
- Concentration
- 1.0 mg/ml
- Storage
- Store at 4C short term. Aliquot and store at -20C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
Submitted references Modulating EGFR-MTORC1-autophagy as a potential therapy for persistent fetal vasculature (PFV) disease.
Assessing the role of toll-like receptor in isolated, standard and enriched housing conditions.
Persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous in two piglets.
A Confocal Reflection Super-Resolution Technique to Image Golgi-Cox Stained Neurons.
Hypoxia regulates the level of glutamic acid decarboxylase enzymes and interrupts inhibitory synapse stability in primary cultured neurons.
Blockade of P2X4 Receptors Inhibits Neuropathic Pain-Related Behavior by Preventing MMP-9 Activation and, Consequently, Pronociceptive Interleukin Release in a Rat Model.
Parvalbumin-expressing ependymal cells in rostral lateral ventricle wall adhesions contribute to aging-related ventricle stenosis in mice.
LRRK2 interferes with aggresome formation for autophagic clearance.
Expression of CYP 4A ω-hydroxylase and formation of 20-hydroxyeicosatetreanoic acid (20-HETE) in cultured rat brain astrocytes.
Nociceptive and sympathetic innervations in the abaxial part of the cranial horn of the equine medial meniscus: an immunohistochemical approach.
De novo expression of parvalbumin in ependymal cells in response to brain injury promotes ependymal remodeling and wound repair.
Notch1 activity in the olfactory bulb is odour-dependent and contributes to olfactory behaviour.
Yazdankhah M, Shang P, Ghosh S, Bhutto IA, Stepicheva N, Grebe R, Hose S, Weiss J, Luo T, Mishra S, Riazuddin SA, Ghosh A, Handa JT, Lutty GA, Zigler JS Jr, Sinha D
Autophagy 2020 Jun;16(6):1130-1142
Autophagy 2020 Jun;16(6):1130-1142
Assessing the role of toll-like receptor in isolated, standard and enriched housing conditions.
Alshammari TK, Alghamdi H, Green TA, Niazy A, Alkahdar L, Alrasheed N, Alhosaini K, Alswayyed M, Elango R, Laezza F, Alshammari MA, Yacoub H
PloS one 2019;14(10):e0222818
PloS one 2019;14(10):e0222818
Persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous in two piglets.
Murakami T, Miyoshi T, Takahashi N, Kangawa A
The Journal of veterinary medical science 2019 Mar 14;81(3):357-360
The Journal of veterinary medical science 2019 Mar 14;81(3):357-360
A Confocal Reflection Super-Resolution Technique to Image Golgi-Cox Stained Neurons.
Sivaguru M, Khaw YM, Inoue M
Journal of microscopy 2019 Aug;275(2):115-130
Journal of microscopy 2019 Aug;275(2):115-130
Hypoxia regulates the level of glutamic acid decarboxylase enzymes and interrupts inhibitory synapse stability in primary cultured neurons.
Hwang S, Ham S, Lee SE, Lee Y, Lee GH
Neurotoxicology 2018 Mar;65:221-230
Neurotoxicology 2018 Mar;65:221-230
Blockade of P2X4 Receptors Inhibits Neuropathic Pain-Related Behavior by Preventing MMP-9 Activation and, Consequently, Pronociceptive Interleukin Release in a Rat Model.
Jurga AM, Piotrowska A, Makuch W, Przewlocka B, Mika J
Frontiers in pharmacology 2017;8:48
Frontiers in pharmacology 2017;8:48
Parvalbumin-expressing ependymal cells in rostral lateral ventricle wall adhesions contribute to aging-related ventricle stenosis in mice.
Filice F, Celio MR, Babalian A, Blum W, Szabolcsi V
The Journal of comparative neurology 2017 Oct 15;525(15):3266-3285
The Journal of comparative neurology 2017 Oct 15;525(15):3266-3285
LRRK2 interferes with aggresome formation for autophagic clearance.
Bang Y, Kim KS, Seol W, Choi HJ
Molecular and cellular neurosciences 2016 Sep;75:71-80
Molecular and cellular neurosciences 2016 Sep;75:71-80
Expression of CYP 4A ω-hydroxylase and formation of 20-hydroxyeicosatetreanoic acid (20-HETE) in cultured rat brain astrocytes.
Gebremedhin D, Zhang DX, Carver KA, Rau N, Rarick KR, Roman RJ, Harder DR
Prostaglandins & other lipid mediators 2016 Jul;124:16-26
Prostaglandins & other lipid mediators 2016 Jul;124:16-26
Nociceptive and sympathetic innervations in the abaxial part of the cranial horn of the equine medial meniscus: an immunohistochemical approach.
Nemery E, Gabriel A, Piret J, Antoine N
Journal of anatomy 2016 Dec;229(6):791-799
Journal of anatomy 2016 Dec;229(6):791-799
De novo expression of parvalbumin in ependymal cells in response to brain injury promotes ependymal remodeling and wound repair.
Szabolcsi V, Celio MR
Glia 2015 Apr;63(4):567-94
Glia 2015 Apr;63(4):567-94
Notch1 activity in the olfactory bulb is odour-dependent and contributes to olfactory behaviour.
Brai E, Marathe S, Zentilin L, Giacca M, Nimpf J, Kretz R, Scotti A, Alberi L
The European journal of neuroscience 2014 Nov;40(10):3436-49
The European journal of neuroscience 2014 Nov;40(10):3436-49
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Novus Biologicals (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Simple Western: GFAP Antibody (5C10) [NBP1-05197] - Simple Western lane view shows a specific band for GFAP in 0.05 mg/ml of Human Brain lysate. This experiment was performed under reducing conditions using the 12-230 kDa separation system.
- Submitted by
- Novus Biologicals (provider)
- Main image
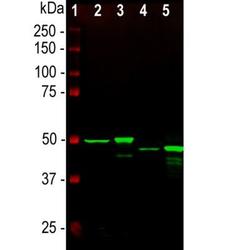
- Experimental details
- Western Blot: GFAP Antibody (5C10) [NBP1-05197] - Analysis of whole tissue lysates using mouse mAb to GFAP, NBP1-05197, dilution 1:2,000, in green: [1] protein standard (red), [2] rat brain, [3] rat spinal cord, [4] mouse brain, [5] mouse spinal cord. The strong band at about 50kDa corresponds to the GFAP protein.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Novus Biologicals (provider)
- Main image
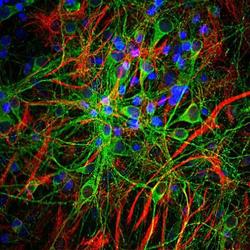
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry: GFAP Antibody (5C10) [NBP1-05197] - Analysis of rat cerebellum section stained with mouse mAb to GFAP, NBP1-05197, dilution 1:1,000, in green, costained with rabbit pAb to neurofilament NF-L, dilution 1:2,000, in red. Following transcardial perfusion of rat with 4% paraformaldehyde, brain was post fixed for 24 hours, cut to 45uM, and free-floating sections were stained with above antibodies. The NBP1-05197 antibody stains a network of astroglial cells, while the NF-L antibody labels neuronal cells and their processes.
- Submitted by
- Novus Biologicals (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry: GFAP Antibody (5C10) [NBP1-05197] - The immunofluorescence of TLR7 recognized by Alexa 488, green (NBP2-24906). GFAP recognized by Alexa 594, red. NEUN recognized by Alexa 633, (blue) and merged image in the hippocampal region. NeuN and GFAP were applied to show the distribution of TLR7 within neuronal and supportive tissue populations. Scale bar 80 um. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (//doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0222818) licensed under a CC-BY licence.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Novus Biologicals (provider)
- Main image
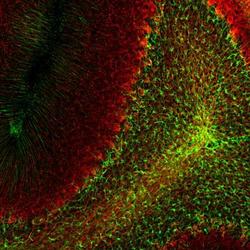
- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry Free-Floating: GFAP Antibody (5C10) [NBP1-05197] - Analysis of rat cerebellum section stained with mouse GFAP mAb, dilution 1:1,000 (Green), costained with rabbit neurofilament NF-L pAb, dilution 1:2,000 (Red). Following transcardial perfusion with 4% paraformaldehyde, brain was post fixed for 24hrs, cut to 45uM, and free-floating sections were stained with antibodies. The GFAP antibody stains a network of astroglial cells, while the NF-L antibody labels neuronal cells and their processes.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry