Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [36]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Western blot [4]
- Immunohistochemistry [1]
- Flow cytometry [1]
- Other assay [1]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- MA5-12717 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- Cyclin D3 Monoclonal Antibody (DCS-22)
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Purifed from natural sources
- Description
- MA5-12717 targets Cyclin D3 in FACS, IF, IHC (P), IP, and WB applications and shows reactivity with Human, mouse, Non-human primate, and Rat samples. The MA5-12717 immunogen is purified human recombinant full length cyclin D3 protein.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- DCS-22
- Vial size
- 500 µL
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/mL
- Storage
- 4° C
Submitted references A Proteomic Survey Indicates Sortilin as a Secondary Substrate of the ER Translocation Inhibitor Cyclotriazadisulfonamide (CADA).
The CDK4/CDK6 inhibitor PD0332991 paradoxically stabilizes activated cyclin D3-CDK4/6 complexes.
Inhibition of mutant BRAF splice variant signaling by next-generation, selective RAF inhibitors.
CDK4 T172 phosphorylation is central in a CDK7-dependent bidirectional CDK4/CDK2 interplay mediated by p21 phosphorylation at the restriction point.
Alteration of G1/S transition regulators influences recurrences in head and neck squamous carcinomas.
Death effector domain-containing protein (DEDD) is required for uterine decidualization during early pregnancy in mice.
β-catenin/cyclin D1 mediated development of suture mesenchyme in calvarial morphogenesis.
cAMP-dependent activation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in thyroid cells. Implication in mitogenesis and activation of CDK4.
Expression of cyclin D2 is an independent predictor of the development of hepatic metastasis in colorectal cancer.
Differential regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4) and CDK6, evidence that CDK4 might not be activated by CDK7, and design of a CDK6 activating mutation.
Identification of a potent natural triterpenoid inhibitor of proteosome chymotrypsin-like activity and NF-kappaB with antimyeloma activity in vitro and in vivo.
Orphan receptor small heterodimer partner suppresses tumorigenesis by modulating cyclin D1 expression and cellular proliferation.
Nuclear localization of barrier-to-autointegration factor is correlated with progression of S phase in human cells.
Cell cycle regulators and outcome of adjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy in completely resected non-small-cell lung cancer: the International Adjuvant Lung Cancer Trial Biologic Program.
Cyclin D1 is transcriptionally regulated by and required for transformation by activated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.
Regulated activating Thr172 phosphorylation of cyclin-dependent kinase 4(CDK4): its relationship with cyclins and CDK "inhibitors".
Ablation of oncogenic ALK is a viable therapeutic approach for anaplastic large-cell lymphomas.
Differential utilization of cyclin D1 and cyclin D3 in the distinct mitogenic stimulations by growth factors and TSH of human thyrocytes in primary culture.
Nuclear beta-catenin expression is rare and its potential association with short survival in colorectal signet-ring cell carcinoma.
Nuclear beta-catenin expression is rare and its potential association with short survival in colorectal signet-ring cell carcinoma.
Increase in Ara-C cytotoxicity in the presence of valproate, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, is associated with the concurrent expression of cyclin D1 and p27(Kip 1) in acute myeloblastic leukemia cells.
Differential involvement of the actin cytoskeleton in differentiation and mitogenesis of thyroid cells: inactivation of Rho proteins contributes to cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent gene expression but prevents mitogenesis.
Cyclin D1-negative mantle cell lymphoma: a clinicopathologic study based on gene expression profiling.
Expression of D-type cyclins in colon cancer and in cell lines from colon carcinomas.
Cdk6-cyclin D3 activity in murine ES cells is resistant to inhibition by p16(INK4a).
Cdk4 is indispensable for postnatal proliferation of the anterior pituitary.
Differential expression of d-type cyclins in podocytes in vitro and in vivo.
Cyclin D3 is a predictive and prognostic factor in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
Expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27(Kip1) in AIDS-related diffuse large-cell lymphomas is associated with Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1.
In vivo interference with Skp1 function leads to genetic instability and neoplastic transformation.
In vivo interference with Skp1 function leads to genetic instability and neoplastic transformation.
Genetic evidence for the interactions of cyclin D1 and p27(Kip1) in mice.
Differential regulation of p27(Kip1) expression by mitogenic and hypertrophic factors: Involvement of transcriptional and posttranscriptional mechanisms.
Regulation of exit from quiescence by p27 and cyclin D1-CDK4.
Regulation of exit from quiescence by p27 and cyclin D1-CDK4.
Molecular aberrations of the G1-S checkpoint in myxoid and round cell liposarcoma.
Van Puyenbroeck V, Claeys E, Schols D, Bell TW, Vermeire K
Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP 2017 Feb;16(2):157-167
Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP 2017 Feb;16(2):157-167
The CDK4/CDK6 inhibitor PD0332991 paradoxically stabilizes activated cyclin D3-CDK4/6 complexes.
Paternot S, Colleoni B, Bisteau X, Roger PP
Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.) 2014;13(18):2879-88
Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.) 2014;13(18):2879-88
Inhibition of mutant BRAF splice variant signaling by next-generation, selective RAF inhibitors.
Basile KJ, Le K, Hartsough EJ, Aplin AE
Pigment cell & melanoma research 2014 May;27(3):479-84
Pigment cell & melanoma research 2014 May;27(3):479-84
CDK4 T172 phosphorylation is central in a CDK7-dependent bidirectional CDK4/CDK2 interplay mediated by p21 phosphorylation at the restriction point.
Bisteau X, Paternot S, Colleoni B, Ecker K, Coulonval K, De Groote P, Declercq W, Hengst L, Roger PP
PLoS genetics 2013 May;9(5):e1003546
PLoS genetics 2013 May;9(5):e1003546
Alteration of G1/S transition regulators influences recurrences in head and neck squamous carcinomas.
Canzonieri V, Barzan L, Franchin G, Vaccher E, Talamini R, Sulfaro S, Baldassarre G
Journal of cellular physiology 2012 Jan;227(1):233-8
Journal of cellular physiology 2012 Jan;227(1):233-8
Death effector domain-containing protein (DEDD) is required for uterine decidualization during early pregnancy in mice.
Mori M, Kitazume M, Ose R, Kurokawa J, Koga K, Osuga Y, Arai S, Miyazaki T
The Journal of clinical investigation 2011 Jan;121(1):318-27
The Journal of clinical investigation 2011 Jan;121(1):318-27
β-catenin/cyclin D1 mediated development of suture mesenchyme in calvarial morphogenesis.
Mirando AJ, Maruyama T, Fu J, Yu HM, Hsu W
BMC developmental biology 2010 Nov 26;10:116
BMC developmental biology 2010 Nov 26;10:116
cAMP-dependent activation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in thyroid cells. Implication in mitogenesis and activation of CDK4.
Blancquaert S, Wang L, Paternot S, Coulonval K, Dumont JE, Harris TE, Roger PP
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2010 Jul;24(7):1453-68
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2010 Jul;24(7):1453-68
Expression of cyclin D2 is an independent predictor of the development of hepatic metastasis in colorectal cancer.
Sarkar R, Hunter IA, Rajaganeshan R, Perry SL, Guillou P, Jayne DG
Colorectal disease : the official journal of the Association of Coloproctology of Great Britain and Ireland 2010 Apr;12(4):316-23
Colorectal disease : the official journal of the Association of Coloproctology of Great Britain and Ireland 2010 Apr;12(4):316-23
Differential regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4) and CDK6, evidence that CDK4 might not be activated by CDK7, and design of a CDK6 activating mutation.
Bockstaele L, Bisteau X, Paternot S, Roger PP
Molecular and cellular biology 2009 Aug;29(15):4188-200
Molecular and cellular biology 2009 Aug;29(15):4188-200
Identification of a potent natural triterpenoid inhibitor of proteosome chymotrypsin-like activity and NF-kappaB with antimyeloma activity in vitro and in vivo.
Tiedemann RE, Schmidt J, Keats JJ, Shi CX, Zhu YX, Palmer SE, Mao X, Schimmer AD, Stewart AK
Blood 2009 Apr 23;113(17):4027-37
Blood 2009 Apr 23;113(17):4027-37
Orphan receptor small heterodimer partner suppresses tumorigenesis by modulating cyclin D1 expression and cellular proliferation.
Zhang Y, Xu P, Park K, Choi Y, Moore DD, Wang L
Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2008 Jul;48(1):289-98
Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2008 Jul;48(1):289-98
Nuclear localization of barrier-to-autointegration factor is correlated with progression of S phase in human cells.
Haraguchi T, Koujin T, Osakada H, Kojidani T, Mori C, Masuda H, Hiraoka Y
Journal of cell science 2007 Jun 15;120(Pt 12):1967-77
Journal of cell science 2007 Jun 15;120(Pt 12):1967-77
Cell cycle regulators and outcome of adjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy in completely resected non-small-cell lung cancer: the International Adjuvant Lung Cancer Trial Biologic Program.
Filipits M, Pirker R, Dunant A, Lantuejoul S, Schmid K, Huynh A, Haddad V, André F, Stahel R, Pignon JP, Soria JC, Popper HH, Le Chevalier T, Brambilla E
Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2007 Jul 1;25(19):2735-40
Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2007 Jul 1;25(19):2735-40
Cyclin D1 is transcriptionally regulated by and required for transformation by activated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.
Leslie K, Lang C, Devgan G, Azare J, Berishaj M, Gerald W, Kim YB, Paz K, Darnell JE, Albanese C, Sakamaki T, Pestell R, Bromberg J
Cancer research 2006 Mar 1;66(5):2544-52
Cancer research 2006 Mar 1;66(5):2544-52
Regulated activating Thr172 phosphorylation of cyclin-dependent kinase 4(CDK4): its relationship with cyclins and CDK "inhibitors".
Bockstaele L, Kooken H, Libert F, Paternot S, Dumont JE, de Launoit Y, Roger PP, Coulonval K
Molecular and cellular biology 2006 Jul;26(13):5070-85
Molecular and cellular biology 2006 Jul;26(13):5070-85
Ablation of oncogenic ALK is a viable therapeutic approach for anaplastic large-cell lymphomas.
Piva R, Chiarle R, Manazza AD, Taulli R, Simmons W, Ambrogio C, D'Escamard V, Pellegrino E, Ponzetto C, Palestro G, Inghirami G
Blood 2006 Jan 15;107(2):689-97
Blood 2006 Jan 15;107(2):689-97
Differential utilization of cyclin D1 and cyclin D3 in the distinct mitogenic stimulations by growth factors and TSH of human thyrocytes in primary culture.
Paternot S, Dumont JE, Roger PP
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2006 Dec;20(12):3279-92
Molecular endocrinology (Baltimore, Md.) 2006 Dec;20(12):3279-92
Nuclear beta-catenin expression is rare and its potential association with short survival in colorectal signet-ring cell carcinoma.
Wong SC, Chan AT, Lo ES, Lo YM
Applied immunohistochemistry & molecular morphology : AIMM 2005 Sep;13(3):248-51
Applied immunohistochemistry & molecular morphology : AIMM 2005 Sep;13(3):248-51
Nuclear beta-catenin expression is rare and its potential association with short survival in colorectal signet-ring cell carcinoma.
Wong SC, Chan AT, Lo ES, Lo YM
Applied immunohistochemistry & molecular morphology : AIMM 2005 Sep;13(3):248-51
Applied immunohistochemistry & molecular morphology : AIMM 2005 Sep;13(3):248-51
Increase in Ara-C cytotoxicity in the presence of valproate, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, is associated with the concurrent expression of cyclin D1 and p27(Kip 1) in acute myeloblastic leukemia cells.
Siitonen T, Koistinen P, Savolainen ER
Leukemia research 2005 Nov;29(11):1335-42
Leukemia research 2005 Nov;29(11):1335-42
Differential involvement of the actin cytoskeleton in differentiation and mitogenesis of thyroid cells: inactivation of Rho proteins contributes to cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent gene expression but prevents mitogenesis.
Fortemaison N, Blancquaert S, Dumont JE, Maenhaut C, Aktories K, Roger PP, Dremier S
Endocrinology 2005 Dec;146(12):5485-95
Endocrinology 2005 Dec;146(12):5485-95
Cyclin D1-negative mantle cell lymphoma: a clinicopathologic study based on gene expression profiling.
Fu K, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC, Dave S, Wright G, Rosenwald A, Chiorazzi M, Iqbal J, Gesk S, Siebert R, De Jong D, Jaffe ES, Wilson WH, Delabie J, Ott G, Dave BJ, Sanger WG, Smith LM, Rimsza L, Braziel RM, Müller-Hermelink HK, Campo E, Gascoyne RD, Staudt LM, Chan WC, Lymphoma/Leukemia Molecular Profiling Project
Blood 2005 Dec 15;106(13):4315-21
Blood 2005 Dec 15;106(13):4315-21
Expression of D-type cyclins in colon cancer and in cell lines from colon carcinomas.
Mermelshtein A, Gerson A, Walfisch S, Delgado B, Shechter-Maor G, Delgado J, Fich A, Gheber L
British journal of cancer 2005 Aug 8;93(3):338-45
British journal of cancer 2005 Aug 8;93(3):338-45
Cdk6-cyclin D3 activity in murine ES cells is resistant to inhibition by p16(INK4a).
Faast R, White J, Cartwright P, Crocker L, Sarcevic B, Dalton S
Oncogene 2004 Jan 15;23(2):491-502
Oncogene 2004 Jan 15;23(2):491-502
Cdk4 is indispensable for postnatal proliferation of the anterior pituitary.
Jirawatnotai S, Aziyu A, Osmundson EC, Moons DS, Zou X, Kineman RD, Kiyokawa H
The Journal of biological chemistry 2004 Dec 3;279(49):51100-6
The Journal of biological chemistry 2004 Dec 3;279(49):51100-6
Differential expression of d-type cyclins in podocytes in vitro and in vivo.
Petermann A, Hiromura K, Pippin J, Blonski M, Couser WG, Kopp J, Mundel P, Shankland SJ
The American journal of pathology 2004 Apr;164(4):1417-24
The American journal of pathology 2004 Apr;164(4):1417-24
Cyclin D3 is a predictive and prognostic factor in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
Filipits M, Jaeger U, Pohl G, Stranzl T, Simonitsch I, Kaider A, Skrabs C, Pirker R
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2002 Mar;8(3):729-33
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2002 Mar;8(3):729-33
Expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27(Kip1) in AIDS-related diffuse large-cell lymphomas is associated with Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1.
Gloghini A, Gaidano G, Larocca LM, Pierconti F, Cingolani A, Dal Maso L, Capello D, Franceschi S, Tirelli U, Libra M, Niu H, Dalla-Favera R, Carbone A
The American journal of pathology 2002 Jul;161(1):163-71
The American journal of pathology 2002 Jul;161(1):163-71
In vivo interference with Skp1 function leads to genetic instability and neoplastic transformation.
Piva R, Liu J, Chiarle R, Podda A, Pagano M, Inghirami G
Molecular and cellular biology 2002 Dec;22(23):8375-87
Molecular and cellular biology 2002 Dec;22(23):8375-87
In vivo interference with Skp1 function leads to genetic instability and neoplastic transformation.
Piva R, Liu J, Chiarle R, Podda A, Pagano M, Inghirami G
Molecular and cellular biology 2002 Dec;22(23):8375-87
Molecular and cellular biology 2002 Dec;22(23):8375-87
Genetic evidence for the interactions of cyclin D1 and p27(Kip1) in mice.
Tong W, Pollard JW
Molecular and cellular biology 2001 Feb;21(4):1319-28
Molecular and cellular biology 2001 Feb;21(4):1319-28
Differential regulation of p27(Kip1) expression by mitogenic and hypertrophic factors: Involvement of transcriptional and posttranscriptional mechanisms.
Servant MJ, Coulombe P, Turgeon B, Meloche S
The Journal of cell biology 2000 Feb 7;148(3):543-56
The Journal of cell biology 2000 Feb 7;148(3):543-56
Regulation of exit from quiescence by p27 and cyclin D1-CDK4.
Ladha MH, Lee KY, Upton TM, Reed MF, Ewen ME
Molecular and cellular biology 1998 Nov;18(11):6605-15
Molecular and cellular biology 1998 Nov;18(11):6605-15
Regulation of exit from quiescence by p27 and cyclin D1-CDK4.
Ladha MH, Lee KY, Upton TM, Reed MF, Ewen ME
Molecular and cellular biology 1998 Nov;18(11):6605-15
Molecular and cellular biology 1998 Nov;18(11):6605-15
Molecular aberrations of the G1-S checkpoint in myxoid and round cell liposarcoma.
Dei Tos AP, Piccinin S, Doglioni C, Vukosavljevic T, Mentzel T, Boiocchi M, Fletcher CD
The American journal of pathology 1997 Dec;151(6):1531-9
The American journal of pathology 1997 Dec;151(6):1531-9
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Western blot analysis was performed on whole cell extracts (30 µg lysate) of A549 (Lane 1) and HEL 92.1.7 (Lane 2). The blots were probed with Anti-Cyclin D3 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (Product # MA5-12717, 1:500-1:2000 dilution) and detected by chemiluminescence using Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody, HRP conjugate (Product # 62-6520, 1:4000 dilution). A 32 kDa band corresponding to Cyclin D3 was observed across cell lines tested. Known quantity of protein samples were electrophoresed using Novex® NuPAGE® 10 % Bis-Tris gel (Product # NP0302BOX), XCell SureLock™ Electrophoresis System (Product # EI0002) and Novex® Sharp Pre-Stained Protein Standard (Product # LC5800). Resolved proteins were then onto a transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane with iBlot® 2 Dry Blotting System (Product # IB21001). The membrane was probed with the relevant primary and secondary Antibody following blocking with 5 % skimmed milk. Chemiluminescent detection was performed using Pierce™ ECL Western Blotting Substrate (Product # 32106).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
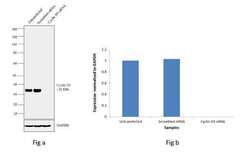
- Experimental details
- Knockdown of Cyclin D3 was achieved by transfecting A549 cells with Cyclin D3 specific validated siRNAs (Silencer® select Product # s2522). Western blot analysis (Fig. a) was performed using modified whole cell extracts (1% SDS) from the Cyclin D3 knockdown cells (lane 3), non-specific scrambled siRNA transfected cells (lane 2) and untransfected cells (lane 1). The blots were probed with Cyclin D3 Monoclonal Antibody (Product # MA5-12717, 1 µg/mL) and Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Superclonal™ Secondary Antibody, HRP conjugate (Product # A28177, 0.25 µg/mL, 1:4000 dilution). Densitometric analysis of this western blot is shown in histogram (Fig. b). Decrease in signal upon siRNA mediated knock down confirms that antibody is specific to Cyclin D3.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
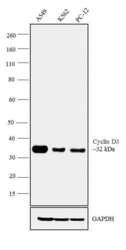
- Experimental details
- Western blot analysis was performed on modified whole cell extracts (1% SDS) of A549 (Lane 1), K562 (Lane 2) and PC-12 (Lane 3). The blot was probed with Anti-Cyclin D3 antibody (Product # MA5-12717, 1 µg/mL) and detected by chemiluminescence using Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Superclonal™ Secondary Antibody, HRP conjugate (Product # A28177, 0.25 µg/mL, 1:4000 dilution). A 32 kDa band corresponding to Cyclin D3 was observed across the cell lines tested.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
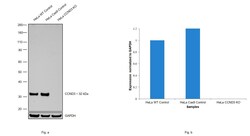
- Experimental details
- Knockout of CCND3 was achieved by CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing using LentiArray™ Lentiviral sgRNA (Product # A32042) (Assay ID CRISPR796863_LV) and LentiArray Cas9 Lentivirus (Product # A32064). Western blot analysis of CCND3 was performed by loading 30 µg of HeLa wild type (Lane 1), HeLa CAS9 (Lane 2), HeLa CCND3 KO (Lane 3) whole cell extracts. The blot was probed with Anti-Cyclin D3 Monoclonal Antibody (DCS-22)(Product # MA5-12717) using 1 µg/mL dilution and Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L), Superclonal™ Recombinant Secondary Antibody, HRP (Product # A28177). Loss of signal upon CRISPR mediated knockout (KO) using the LentiArray™ CRISPR product line confirms that antibody is specific to CCND3.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human tonsil stained with Cyclin D3 antibody using peroxidase-conjugate and AEC chromogen. Note nuclear staining of cells.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of Cyclin D3 was done on A549 cells. Cells were fixed with 70% ethanol for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.25% Triton™ X-100 for 20 minutes, and blocked with 5% BSA for 30 minutes at room temperature. Cells were labeled with Cyclin D3 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (MA512717, red histogram) or with mouse isotype control (yellow histogram) at 3-5 ug/million cells in 2.5% BSA. After incubation at room temperature for 2 hours, the cells were labeled with Alexa Fluor® 488 Rabbit Anti-Mouse Secondary Antibody (A11059) at a dilution of 1:400 for 30 minutes at room temperature. The representative 10,000 cells were acquired and analyzed for each sample using an Attune® Acoustic Focusing Cytometer. The purple histogram represents unstained control cells and the green histogram represents no-primary-antibody control.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Immunoprecipitation of Cyclin D3 using Cyclin D3 Monoclonal Antibody (Product # MA5-12717) on Native Human LS174T Cells.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Immunoprecipitation
Immunoprecipitation