ABIN955007
antibody from antibodies-online
Targeting: SUMO1
GMP1, OFC10, PIC1, SMT3C, SMT3H3, SUMO-1, UBL1
Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [5]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Western blot [1]
- Immunohistochemistry [1]
- Flow cytometry [1]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- ABIN955007 - Provider product page

- Provider
- antibodies-online
- Product name
- anti-SMT3 Suppressor of Mif Two 3 Homolog 1 (S. Cerevisiae) (SUMO1) antibody
- Antibody type
- Polyclonal
- Description
- Affinity chromatography on Protein A
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Rabbit
- Vial size
- 0.4 mL
- Storage
- Store the antibody undiluted at 2-8°C for one month or (in aliquots) at -20°C for longer.
- Handling
- Avoid repeated freezing and thawing.
Submitted references Modification of de novo DNA methyltransferase 3a (Dnmt3a) by SUMO-1 modulates its interaction with histone deacetylases (HDACs) and its capacity to repress transcription.
Characterization of the localization and proteolytic activity of the SUMO-specific protease, SENP1.
SUMO promotes HDAC-mediated transcriptional repression.
SUMO-1 marks the nuclear inclusions in familial neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease.
Transforming growth factor-beta-mediated signaling via the p38 MAP kinase pathway activates Smad-dependent transcription through SUMO-1 modification of Smad4.
Ling Y, Sankpal UT, Robertson AK, McNally JG, Karpova T, Robertson KD
Nucleic acids research 2004;32(2):598-610
Nucleic acids research 2004;32(2):598-610
Characterization of the localization and proteolytic activity of the SUMO-specific protease, SENP1.
Bailey D, O'Hare P
The Journal of biological chemistry 2004 Jan 2;279(1):692-703
The Journal of biological chemistry 2004 Jan 2;279(1):692-703
SUMO promotes HDAC-mediated transcriptional repression.
Yang SH, Sharrocks AD
Molecular cell 2004 Feb 27;13(4):611-7
Molecular cell 2004 Feb 27;13(4):611-7
SUMO-1 marks the nuclear inclusions in familial neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease.
Pountney DL, Huang Y, Burns RJ, Haan E, Thompson PD, Blumbergs PC, Gai WP
Experimental neurology 2003 Nov;184(1):436-46
Experimental neurology 2003 Nov;184(1):436-46
Transforming growth factor-beta-mediated signaling via the p38 MAP kinase pathway activates Smad-dependent transcription through SUMO-1 modification of Smad4.
Ohshima T, Shimotohno K
The Journal of biological chemistry 2003 Dec 19;278(51):50833-42
The Journal of biological chemistry 2003 Dec 19;278(51):50833-42
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- antibodies-online (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- WB
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- antibodies-online (provider)
- Main image
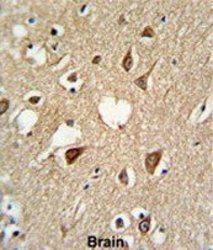
- Experimental details
- IHC
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- antibodies-online (provider)
- Main image
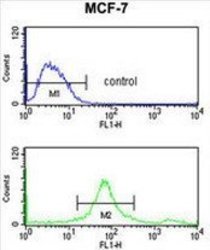
- Experimental details
- FACS
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot