MA3-914
antibody from Invitrogen Antibodies
Targeting: ATP2B4
ATP2B2, MXRA1, PMCA4
 Western blot
Western blot Immunocytochemistry
Immunocytochemistry Immunoprecipitation
Immunoprecipitation Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry Other assay
Other assayAntibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [0]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Western blot [1]
- Immunocytochemistry [6]
- Immunohistochemistry [5]
- Flow cytometry [4]
- Other assay [19]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- MA3-914 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- PMCA ATPase Monoclonal Antibody (5F10)
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Purifed from natural sources
- Description
- MA3-914 detects calcium pump of the plasma membrane (PMCA) ATPase from amphibian, canine, chicken, feline, human, mouse, sheep, primate, rabbit, and rat tissues. This antibody detects all four known isoforms of the PMCA ATPase. MA3-914 has been successfully used in Western blot, FACS, immunohistochemistry, immunocytochemistry, immunofluorescence and immunoprecipitation procedures. By Western blot, this antibody recognizes an ~140 kDa protein representing PMCA ATPase and bands at 95kDa and 180 kDa which probably represent products of aggregation and/or natural proteolytic products of the pump from rat liver membrane preparations. Immunohistochemical staining of PMCA ATPase with MA3-914 yields a pattern consistent with that seen in the literature and depends on the tissue being studied and the localization of the isoforms present. MA3-914 can be used on both frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues. The MA3-914 antigen is purified human erythrocyte calcium ATPase. This antibody recognizes an epitope between amino acids 724-783 of the human erythrocyte calcium pump.
- Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat, Canine, Chicken/Avian, Feline, Rabbit
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- 5F10
- Vial size
- 100 μL
- Concentration
- 1 mg/mL
- Storage
- -20°C, Avoid Freeze/Thaw Cycles
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Western blot analysis of PMCA ATPase was performed by loading 25 µg of U251 (lane 1), human brain (lane 2) and C2C12 (lane 3) onto an SDS polyacrylamide gel. Proteins were transferred to a PVDF membrane and blocked at 4ºC overnight. The membrane was probed with a PMCA ATPase monoclonal antibody (Product # MA3-914) at a dilution of 1:2000 overnight at 4°C, washed in TBST, and probed with an HRP-conjugated secondary antibody for 1 hr at room temperature in the dark. Chemiluminescent detection was performed using Pierce ECL Plus Western Blotting Substrate (Product # 32132). Results show a band at ~140 kDa.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
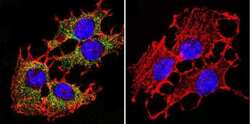
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of PMCA ATPase using Anti-PMCA ATPase Monoclonal Antibody (5F10) (Product # MA3-914) shows staining in C6 Cells. PMCA ATPase staining (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with or an antibody recognizing PMCA ATPase (Product # MA3-914) at a dilution of 1:200 over night at 4°C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35503, Goat Anti-Mouse). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of PMCA ATPase using Anti-PMCA ATPase Monoclonal Antibody (5F10) (Product # MA3-914) shows staining in Hela Cells. PMCA ATPase staining (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with or an antibody recognizing PMCA ATPase (Product # MA3-914) at a dilution of 1:100 over night at 4°C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35503, Goat Anti-Mouse). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of PMCA ATPase using Anti-PMCA ATPase Monoclonal Antibody (5F10) (Product # MA3-914) shows staining in U251 Cells. PMCA ATPase staining (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with or an antibody recognizing PMCA ATPase (Product # MA3-914) at a dilution of 1:200 over night at 4°C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35503, Goat Anti-Mouse). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of PMCA ATPase using Anti-PMCA ATPase Monoclonal Antibody (5F10) (Product # MA3-914) shows staining in C6 Cells. PMCA ATPase staining (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with or an antibody recognizing PMCA ATPase (Product # MA3-914) at a dilution of 1:200 over night at 4°C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35503, Goat Anti-Mouse). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of PMCA ATPase using Anti-PMCA ATPase Monoclonal Antibody (5F10) (Product # MA3-914) shows staining in Hela Cells. PMCA ATPase staining (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with or an antibody recognizing PMCA ATPase (Product # MA3-914) at a dilution of 1:100 over night at 4°C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35503, Goat Anti-Mouse). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescent analysis of PMCA ATPase using Anti-PMCA ATPase Monoclonal Antibody (5F10) (Product # MA3-914) shows staining in U251 Cells. PMCA ATPase staining (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with or an antibody recognizing PMCA ATPase (Product # MA3-914) at a dilution of 1:200 over night at 4°C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product # 35503, Goat Anti-Mouse). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry was performed on normal deparaffinized Human tonsil tissue tissues. To expose target proteins, heat induced antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH6.0) buffer, microwaved for 8-15 minutes. Following antigen retrieval tissues were blocked in 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Tissues were then probed at a dilution of 1:200 with a mouse monoclonal antibody recognizing PMCA ATPase (Product # MA3-914) or without primary antibody (negative control) overnight at 4°C in a humidified chamber. Tissues were washed extensively with PBST and endogenous peroxidase activity was quenched with a peroxidase suppressor. Detection was performed using a biotin-conjugated secondary antibody and SA-HRP, followed by colorimetric detection using DAB. Tissues were counterstained with hematoxylin and prepped for mounting.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry was performed on normal deparaffinized Human brain tissue tissues. To expose target proteins, heat induced antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH6.0) buffer, microwaved for 8-15 minutes. Following antigen retrieval tissues were blocked in 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Tissues were then probed at a dilution of 1:200 with a mouse monoclonal antibody recognizing PMCA ATPase (Product # MA3-914) or without primary antibody (negative control) overnight at 4°C in a humidified chamber. Tissues were washed extensively with PBST and endogenous peroxidase activity was quenched with a peroxidase suppressor. Detection was performed using a biotin-conjugated secondary antibody and SA-HRP, followed by colorimetric detection using DAB. Tissues were counterstained with hematoxylin and prepped for mounting.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry was performed on cancer biopsies of deparaffinized Human colon carcinoma tissues. To expose target proteins, heat induced antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH6.0) buffer, microwaved for 8-15 minutes. Following antigen retrieval tissues were blocked in 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Tissues were then probed at a dilution of 1:100 with a mouse monoclonal antibody recognizing PMCA ATPase (Product # MA3-914) or without primary antibody (negative control) overnight at 4°C in a humidified chamber. Tissues were washed extensively with PBST and endogenous peroxidase activity was quenched with a peroxidase suppressor. Detection was performed using a biotin-conjugated secondary antibody and SA-HRP, followed by colorimetric detection using DAB. Tissues were counterstained with hematoxylin and prepped for mounting.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry was performed on normal deparaffinized Human brain tissue tissues. To expose target proteins, heat induced antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH6.0) buffer, microwaved for 8-15 minutes. Following antigen retrieval tissues were blocked in 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Tissues were then probed at a dilution of 1:200 with a mouse monoclonal antibody recognizing PMCA ATPase (Product # MA3-914) or without primary antibody (negative control) overnight at 4°C in a humidified chamber. Tissues were washed extensively with PBST and endogenous peroxidase activity was quenched with a peroxidase suppressor. Detection was performed using a biotin-conjugated secondary antibody and SA-HRP, followed by colorimetric detection using DAB. Tissues were counterstained with hematoxylin and prepped for mounting.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry was performed on cancer biopsies of deparaffinized Human colon carcinoma tissues. To expose target proteins, heat induced antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH6.0) buffer, microwaved for 8-15 minutes. Following antigen retrieval tissues were blocked in 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Tissues were then probed at a dilution of 1:100 with a mouse monoclonal antibody recognizing PMCA ATPase (Product # MA3-914) or without primary antibody (negative control) overnight at 4°C in a humidified chamber. Tissues were washed extensively with PBST and endogenous peroxidase activity was quenched with a peroxidase suppressor. Detection was performed using a biotin-conjugated secondary antibody and SA-HRP, followed by colorimetric detection using DAB. Tissues were counterstained with hematoxylin and prepped for mounting.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
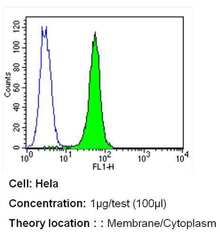
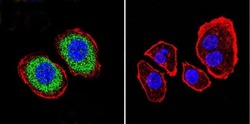
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of PMCA ATPase in Hela cells (green) compared to an isotype control (blue). Cells were harvested, adjusted to a concentration of 1-5x10^6 cells/mL, fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde and washed with PBS. Cells were blocked with a 2% solution of BSA-PBS for 30 min at room temperature and incubated with a PMCA ATPase monoclonal antibody (Product # MA3-914) at a dilution of 1 µg/test for 40 min at room temperature. Cells were then incubated for 40 min at room temperature in the dark using a Dylight 488-conjugated secondary antibody and re-suspended in PBS for FACS analysis.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
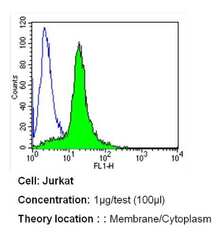
- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of PMCA ATPase in Jurkat cells (green) compared to an isotype control (blue). Cells were harvested, adjusted to a concentration of 1-5x10^6 cells/mL, fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde and washed with PBS. Cells were blocked with a 2% solution of BSA-PBS for 30 min at room temperature and incubated with a PMCA ATPase monoclonal antibody (Product # MA3-914) at a dilution of 1 µg/test for 40 min at room temperature. Cells were then incubated for 40 min at room temperature in the dark using a Dylight 488-conjugated secondary antibody and re-suspended in PBS for FACS analysis.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of PMCA ATPase in Hela cells (green) compared to an isotype control (blue). Cells were harvested, adjusted to a concentration of 1-5x10^6 cells/mL, fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde and washed with PBS. Cells were blocked with a 2% solution of BSA-PBS for 30 min at room temperature and incubated with a PMCA ATPase monoclonal antibody (Product # MA3-914) at a dilution of 1 µg/test for 40 min at room temperature. Cells were then incubated for 40 min at room temperature in the dark using a Dylight 488-conjugated secondary antibody and re-suspended in PBS for FACS analysis.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Flow cytometry analysis of PMCA ATPase in Jurkat cells (green) compared to an isotype control (blue). Cells were harvested, adjusted to a concentration of 1-5x10^6 cells/mL, fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde and washed with PBS. Cells were blocked with a 2% solution of BSA-PBS for 30 min at room temperature and incubated with a PMCA ATPase monoclonal antibody (Product # MA3-914) at a dilution of 1 µg/test for 40 min at room temperature. Cells were then incubated for 40 min at room temperature in the dark using a Dylight 488-conjugated secondary antibody and re-suspended in PBS for FACS analysis.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
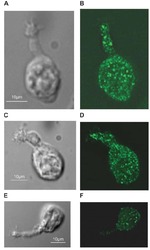
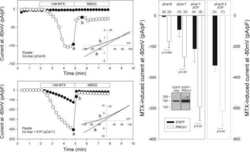
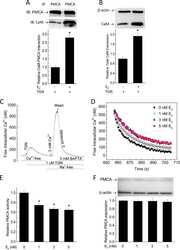
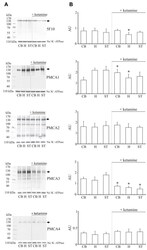
- Figure 4 Western blot analysis of PMCA protein in synaptosomal membranes. The protein level was determined by immunoblotting (A) using 5F10 antibody recognizing all PMCA isoforms as well as isoform-specific antibodies. The intensity of bands was quantitated by densitometry (B) . The results are presented as AU obtained after normalization to endogenous Na + /K + -ATPase level. Representative blots are shown. Arrows indicate bands taken for quantitative analysis. * P < 0.05 ketamine treated vs. saline, n = 5. CB, cerebellum; H, hippocampus; ST, striatum.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
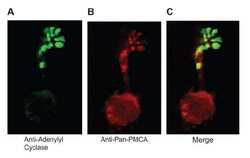
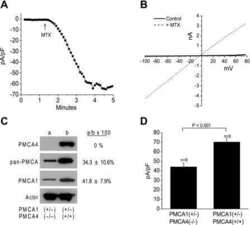
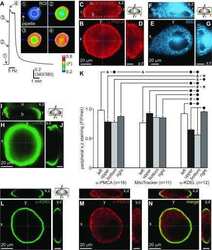
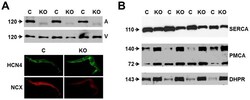
- Figure 1 Expression of NCX1 and other Ca handling proteins in atrial-specific NCX1 knockout mice. A . Immunoblot (top) of mouse atrial (A) and ventricular (V) homogenate using an antibody to NCX1 in wildtype control (C) and atrial-specific NCX1 KO mice. There is complete absence of NCX1 protein in the immunoblot. The new band in the KO lanes at ~110 kDa represents nonfunctional NCX in KO atria after excision of exon 11 by Cre recombinase [13] . Ventricular expression of NCX1 is unaffected in atrial-specific KO mice. The bottom panel shows immunofluorescence of isolated SAN node myocytes from control (C) and KO hearts. Myocytes were co-immunolabled with antibodies against HCN4 and NCX1. Both control and KO SAN cells stained positive for HCN4, but only control SAN cells showed staining of NCX at the membrane. B . Immunoblots of sarcoendoplasmic reticulum Ca ATPase (SERCA), plasma membrane Ca pump (PMCA; the lower band at 72 kDa represents an active proteolytic fragment), and dihydropyridine receptor (DHPR) in control (C) and NCX1 KO atria. Note the reduction in SERCA and the increase in PMCA and DHPR in KO.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
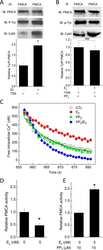
- Figure 4 Western blot analysis of PMCA protein in synaptosomal membranes. The protein level was determined by immunoblotting (A) using 5F10 antibody recognizing all PMCA isoforms as well as isoform-specific antibodies. The intensity of bands was quantitated by densitometry (B) . The results are presented as AU obtained after normalization to endogenous Na + /K + -ATPase level. Representative blots are shown. Arrows indicate bands taken for quantitative analysis. * P < 0.05 ketamine treated vs. saline, n = 5. CB, cerebellum; H, hippocampus; ST, striatum.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
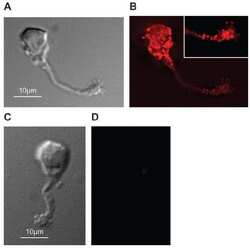
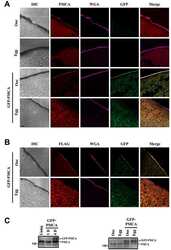
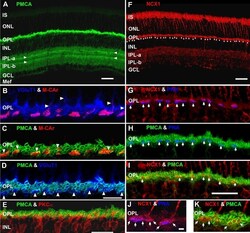
- Figure 7 Lamination patterns and differential compartmentation of pan-plasma membrane Ca 2+ ATPase and Na + -Ca 2+ exchanger isoform 1 in rod spherules and cone pedicles. A : Confocal image of retina immunolabeled for pan-plasma membrane Ca 2+ ATPase (pan-PMCA). The double white arrowheads identify strongly labeled PMCA bands in each IPL sublamina. The scale bar applies to A , D and represents 40 mum. B - D : PMCA preferentially labels rod spherules. OPL double labeled with markers for PMCA (green), vesicular glutamate transporter 1 (VGluT1: blue) and/or M-cone arrestin (M-CAr: red). Scale bar equal 20 mum. B : VGluT1, which labels photoreceptor terminals and M-CAr, which labels cones, colocalize in the OPL. This reveals the large dome-shaped cone pedicles (purple pixels) and some cone axons (white arrowheads). C : This high magnification image shows the horseshoe-like appearance of the PMCA-positive rod spherules. In contrast, the retina double labeled with PMCA and M-CAr shows that cone pedicles stain weakly and diffusely for PMCA, except for a discrete band at the top of the pedicle (white arrowheads: yellow pixels). D : A retina double labeled with PMCA and VGluT1 confirms that PMCA extensively labels rod spherules, but only sparsely labels cone pedicles (white arrowheads). E : PKCalpha-positive rod bipolar cells (red) are pan-PMCA-negative (green), although they are in close apposition around the rod spherules (yellow pixels). The scale bar represents 20 mum. F : Retinal
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
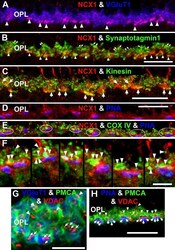
- Figure 8 NCX1 localizes to ribbon synaptic units of cone pedicles and mitochondria closely associate with PMCA in photoreceptor terminals. A : NCX1-positive cone pedicles (red) and VGluT1 (blue) colocalize in the proximal ONL (white arrowheads: purple pixels). B : Synaptotagmin 1 (green) labels photoreceptor synaptic vesicles. Small NCX1- and synaptotagmin 1-positive puncta colocalize in rod spherules (white arrows: yellow pixels), while larger colocalized clusters are present in cone pedicles (white arrowheads: yellow-orange pixels). Scale bar equal 20 mum. C : Kinesin KIF3A (green) labels photoreceptor ribbons and docked synaptic vesicles. The kinesin-labeled rod spherules have an arc-shaped appearance and colocalize with diffusely located NCX1 (small yellow puncta). In contrast, cone pedicles have large clusters of double labeled NCX1- and kinesin-positive puncta (white arrows: yellow-orange pixels). Scale bar equal 20 mum. D - F : Mitochondria cluster away from the active zone in cone pedicles. Scale for D and E equal 20 mum and for F equal 10 mum. D : NCX1 (red) and PNA (blue) colocalize in cone pedicles (purple pixels). E : Triple labeling with NCX1, PNA and COX IV (green) reveals that the cone pedicles (white ellipsoids) contain multiple mitochondria that are located away from the ribbon synaptic unit. F : Higher magnification image of the same six pedicles in E reveals the COX IV and NCX1 colabeling (white arrowheads) and the distance of the COX IV-positive mitochondr
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- Figure EV1 Behavioral characterization of wt mice following striatal infusion of the high dose of cholesterol and in vivo exogenous cholesterol localization A Latency to fall (seconds) from an accelerating rotarod at 10 weeks of age (3 weeks after cholesterol infusion) in wt ( N = 11); wt ACSF ( N = 11) and wt chol-high ( N = 7) mice. B-E Global motor activity (B), total distance travelled (C), mean velocity (D), and stereotyped movements (E) in an open field at 11 weeks of age (4 weeks after cholesterol infusion) (wt = 11; wt ACSF = 10; wt chol-high = 7). F Discrimination index (%) in the novel object recognition test of wt, wt ACSF, and wt chol-high mice at 11 weeks of age (4 weeks after cholesterol infusion) (wt = 11; wt ACSF = 10; wt chol-high = 7). DI above zero indicates a preference for the novel object; DI below zero indicates a preference for the familiar object. G, H Cholesterol content in the infused striatum (G) and ipsilateral cortex (H) of wt ACSF ( N = 3), wt chol-low ( N = 5), and wt chol-high ( N = 4) mice at 12 weeks of age after 4-week striatal cholesterol infusion. I-M Representative confocal images showing co-localization of BODIPY-chol (green) and TGN46 (I), calnexin (J), Rab9 (K), PMCA-ATPase (L), and LAMP1 (M) (red) in the striatum of R6/2 mice infused with BODIPY-cholesterol. Scale bars: 5 mum. Data information: The data in (A-H) are shown as scatterplot graphs with means +- standard error. Each dot corresponds to the value obtained from each animal.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
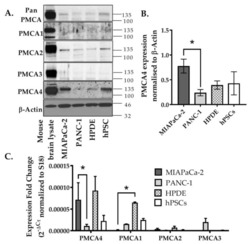
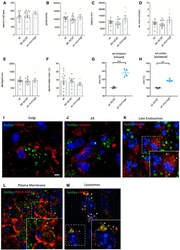
- Experimental details
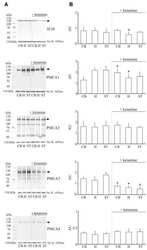
- Figure 2 Expression of PMCA isoforms in multiple pancreatic cell lines. ( A ) Representative Western immunoblot showing the relative protein expression of total/pan-PMCA and PMCA isoform 1-4 in pancreatic cancer (MIA PaCa-2 and PANC-1) and non-malignant pancreatic cells (human pancreatic ductal epithelial (HPDE) and human pancreatic stellate cells (hPSC)). Mouse brain lysate was used as a positive control for PMCA expressions and beta-Actin was used as a protein loading control. ( B ) PMCA4 protein expression in each cell line was quantified from Western blot bands and normalized to beta-Actin housekeeping protein. ( C ) The relative expressions of ATP2B1-4 (PMCA1-4 mRNA) in each cell line were quantified by RT-qPCR. Data are expressed as relative mRNA expression normalized to corresponding S18 rRNA controls (2 -DeltaCtau ). Statistical comparisons were made using the Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn's multiple comparison test and two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett's multiple comparison test. Data are expressed as mean +- SEM. (n = 4-5, 4 replicates per treatment condition). * represents statistical significance where p < 0.05.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
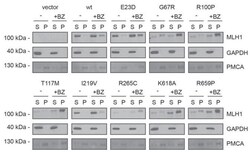
- Experimental details
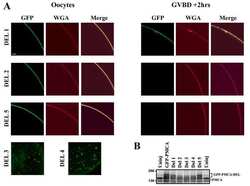
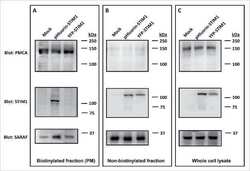
- Figure 3--figure supplement 1. Solubility of selected MLH1 variants. Transfected cells, either untreated (-) or treated for 16 hr with 10 muM bortezomib (+BZ) were lysed by sonication and immediately separated into supernatant ( S ) and pellet ( P ) fractions by centrifugation. Western blotting using antibodies to MLH1 was employed to determine the amount of MLH1 in the fractions. Blotting with antibodies to GAPDH and PMCA served as loading controls for the soluble and insoluble fraction, respectively.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn