Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [5]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Western blot [2]
- Immunocytochemistry [2]
- Immunohistochemistry [1]
- Chromatin Immunoprecipitation [1]
- Other assay [8]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 14-9773-82 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- SOX11 Monoclonal Antibody (SOX11-C1), eBioscience™
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Other
- Description
- Description: The monoclonal antibody SOX11-C1 (C1) recognizes human Sox11. The transcription factor Sox11 is a member of the SOX (sex determining region Y-related HMG (High Mobility Group) Box) family of proteins. Under normal conditions Sox11 is expressed in the developing central nervous system during embryogenesis and has sequence homology to Sox4. Sox11 plays a role in neuronal maturation and epithelial-mesenchymal interactions and is required for the survival of neuronal and mesenchymal progenitor cells. Sox11 is expressed in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) and in subsets of hairy cell leukemias, Burkitt lymphomas, and B cell lymphoblastic leukemias, but is not expressed in other B cell lymphomas or in normal B lymphocytes. Sox11 is also expressed in epithelial ovarian cancer and gliomas. Applications Reported: This SOX11-C1 antibody has been reported for use in flow cytometric analysis, western blotting, immunohistochemical staining of formalin-fixed paraffin embedded tissue sections, and immunocytochemistry. Applications Tested: This SOX11-C1 antibody has been tested by immunohistochemistry of formalin-fixed paraffin embedded tissue using low or high pH antigen retrieval. The antibody can be used at less than or equal to 5 µg/mL. This SOX11-C1 antibody has been tested by immunocytochemistry of fixed and permeabilized cells and can be used at less than or equal to 5 µg/mL. It is recommended that the antibody be carefully titrated for optimal performance in the assay of interest. Purity: Greater than 90%, as determined by SDS-PAGE. Aggregation: Less than 10%, as determined by HPLC. Filtration: 0.2 µm post-manufacturing filtered.
- Reactivity
- Human
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- SOX11-C1
- Vial size
- 100 µg
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/mL
- Storage
- 4° C
Submitted references SOX11 promotes epithelial/mesenchymal hybrid state and alters tropism of invasive breast cancer cells.
The role of SOX11 in mantle cell lymphoma.
Expanded clinical and experimental use of SOX11 - using a monoclonal antibody.
Nuclear expression of the non B-cell lineage Sox11 transcription factor identifies mantle cell lymphoma.
Expression of the Sox11 gene in mouse embryos suggests roles in neuronal maturation and epithelio-mesenchymal induction.
Oliemuller E, Newman R, Tsang SM, Foo S, Muirhead G, Noor F, Haider S, Aurrekoetxea-Rodríguez I, Vivanco MD, Howard BA
eLife 2020 Sep 10;9
eLife 2020 Sep 10;9
The role of SOX11 in mantle cell lymphoma.
Lu TX, Li JY, Xu W
Leukemia research 2013 Nov;37(11):1412-9
Leukemia research 2013 Nov;37(11):1412-9
Expanded clinical and experimental use of SOX11 - using a monoclonal antibody.
Nordström L, Andréasson U, Jerkeman M, Dictor M, Borrebaeck C, Ek S
BMC cancer 2012 Jun 27;12:269
BMC cancer 2012 Jun 27;12:269
Nuclear expression of the non B-cell lineage Sox11 transcription factor identifies mantle cell lymphoma.
Ek S, Dictor M, Jerkeman M, Jirström K, Borrebaeck CA
Blood 2008 Jan 15;111(2):800-5
Blood 2008 Jan 15;111(2):800-5
Expression of the Sox11 gene in mouse embryos suggests roles in neuronal maturation and epithelio-mesenchymal induction.
Hargrave M, Wright E, Kun J, Emery J, Cooper L, Koopman P
Developmental dynamics : an official publication of the American Association of Anatomists 1997 Oct;210(2):79-86
Developmental dynamics : an official publication of the American Association of Anatomists 1997 Oct;210(2):79-86
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
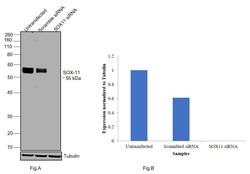
- Experimental details
- Knockdown of SOX11 was achieved by transfecting SH-SY5Y with SOX11 specific siRNAs (Silencer® select Product # s224668, s194808) . Western blot analysis (Fig. a) was performed using modified whole cell extracts (1% SDS) from the SOX11 knockdown cells (Lane 3), non-specific scrambled siRNA transfected cells (Lane 2) and untransfected cells (Lane 1). The blot was probed with SOX11 Monoclonal Antibody (SOX11-C1), eBioscience™ (Product # 14-9773-82, 1:1000 dilution) and Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Superclonal™ Recombinant Secondary Antibody, HRP (Product # A28177, 1:4000 dilution). Densitometric analysis of this western blot is shown i histogram (Fig. b). Loss of signal upon siRNA mediated knock down confirms that antibody is specific to SOX11.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Western blot was performed using SOX11 Monoclonal Antibody (SOX11-C1), eBioscience™ (Product # 14-9773-82) and a 55 kDa band corresponding to SOX11 was observed across cell lines tested except BeWo and HL-60 which are reported to be negative. Whole cell extracts (30 µg lysate) of SHSY-5Y (Lane 1), IMR-32 (Lane 2), BeWo (Lane 3) HL-60 (Lane 4) were electrophoresed using NuPAGE® 4-12 % Bis-Tris gel (Product # NP0321BOX). Resolved proteins were then transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane (Product # IB23001) by iBlot® 2 Dry Blotting System (Product # IB21001). The blot was probed with the primary antibody (1:1000 dilution) and detected by chemiluminescence with Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Superclonal™ Recombinant Secondary Antibody, HRP (Product # A28177, 1:4000 dilution) using the iBright FL 1000 (Product # A32752). Chemiluminescent detection was performed using Novex® ECL Chemiluminescent Substrate Reagent Kit (Product # WP20005).
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
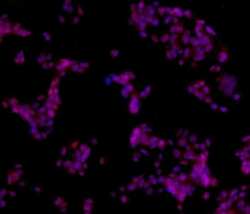
- Experimental details
- Immunocytochemistry of fixed and permeabilized HepG2 cells using 10 µg/mL of Anti-Human Sox11 Purified followed by F (ab')2 Anti-Mouse IgG eFluor® 570.Nuclei are stained with DAPI, colocalization appears pink.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
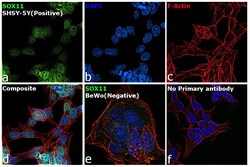
- Experimental details
- Immunofluorescence analysis of SOX11 was performed using 70% confluent log phase SHSY-5Y and BeWo cells. The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 minutes, permeabilized with 0.1% Triton™ X-100 for 15 minutes, and blocked with 2% BSA for 1 hour at room temperature. The cells were labeled with SOX11 Monoclonal Antibody (SOX11-C1), eBioscience™ (Product # 14-9773-82) at 5 µg/mL concentration in 0.1% BSA, incubated at 4 degree Celsius overnight and then labeled with Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Superclonal™ Recombinant Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor® 488 (Product # A27034) at a dilution of 1:2000 for 45 minutes at room temperature (Panel a: green). Nuclei (Panel b: blue) were stained with SlowFade® Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (Product # S36938). F-actin (Panel c: red) was stained with Rhodamine Phalloidin (Product # R415, 1:300). Panel d represents the merged image showing localization to nucleus. Panel e shows BeWo cells with no expression of SOX11. Panel f represents control cells with no primary antibody to assess background. The images were captured at 60X magnification.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Immunohistochemistry of formalin-fixed paraffin embedded human Mantle Cell lymphoma using 10 µg/mL of Anti-Human Sox11 Purified followed by Anti-Mouse IgG Biotin, Streptavidin HRP, and DAB visualization.Nuclei are counterstained with hematoxylin.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
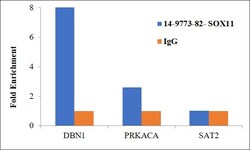
- Experimental details
- Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay of endogenous SOX11 protein using Anti-SOX11 Antibody: ChIP was performed using Anti-SOX11 Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (Product # 14-9773-82) 5 µg, on sheared chromatin from SH-SY5Y cells using the MAGnify ChIP System kit (Product # 49-2024). Normal Mouse IgG was used as a negative IP control. The purified DNA was analyzed by qPCR using primers binding to transcriptional start site of DBN1, PRKACA and SAT2 satellite repeats. Data is presented as fold enrichment of the antibody signal versus the negative control IgG using the comparative CT method.
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
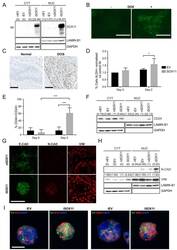
- Experimental details
- Figure 1. Inducible expression of SOX11 leads to changes in cell state profiles of DCIS.com cells. ( A ) Western blot of SOX11 in cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of DCIS.com cells containing the pInducer21 empty vector in presence (iEV) or absence (niEV) of 1 muM Doxycycline (DOX) or the pInducer21SOX11 with (iSOX11) or without DOX (niSOX11). GAPDH and LAMIN B1 were used as loading control of cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions, respectively. Densitometry results normalised against niSOX11 are shown in brackets. ( B ) SOX11 expression detected in iSOX11 cells stained by IF after 48 hr of DOX induction. Scale Bar: 200 mum. ( C ) ER- DCIS case sample showing SOX11 staining in DCIS and adjacent normal breast tissue. Scale Bar: 200 mum. ( D ) Results from flow cytometry analysis of Aldefluor assays of niEV and niSOX11 cells (day 0) and iEV and iSOX11 after 2 days treatment with 1 muM DOX. Results show the % of ALDH+ cells normalised against niEV. Error bars represent SD. *p = 0.0223. n = 5. ( E ) Results from flow cytometry analysis of CD24 and CD44 of niEV and niSOX11 cells (day 0) and iEV and iSOX11 after treatment with 1 muM DOX for 2 days. Results show the average % of cells CD44+/CD24+ in each condition. Error bars represent SD. ***p = 0.0005 (iSOX11 vs niSOX11) and p = 0.0009 (iSOX11 vs iEV) n = 3. ( F ) Western blot of CD24 in cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of niEV, niSOX11, iEV and iSOX11 cells. GAPDH and LAMIN B1 were used as loading control of cytoplasmic and nuclear
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
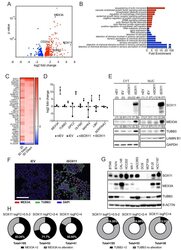
- Experimental details
- Figure 3. SOX11 expression promotes expression of developmental pathways frequently activated in cancer. ( A ) Volcano plot representing the RNAs with a log2 fold-change > +/- 0.585 in the RNA-sequencing results of iSOX11 cells grown in 2D compared with the controls [(iSOX11-niSOX11)- (iEV-niEV)] to account for effects of DOX treatment on DCIS.com cells. ( B ) Gene ontology results from A. ( C ) List of genes overexpressed log2 fold-change >+/-1.585 times in all three RNA-sequencing (cells grown in: 2D, 3D for 2 days, 3D for 5 days) results comparing iSOX11 versus iEV. ( D ) qRT-PCR results for several potential SOX11 targets in EV and SOX11 cells with and without DOX induction in cells grown in 2D. Experiment was repeated three times. ( E ) Western blot of MEX3A and TUBB3 in cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of EV or SOX11 cells in presence or absence of 1 muM DOX. GAPDH and LAMIN B1 were used as loading control of cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions respectively. In brackets, densitometry results normalised against niEV and niSOX11. ( F ) IF staining of DCIS iEV and DCIS iSOX11 cells with TUBB3 (green) and MEX3A (red). Scale: 200 mum. ( G ) Western blot of MEX3A and TUBB3 in SOX11+ breast cancer cell lines and SOX11- DCIS.com and MCF10A from the MCF10A mammary cell progression series. ( H ) Pie charts representing the percentage of breast cancer samples with a log2 fold-change greater than two in the levels of MEX3A or TUBB3 RNA when SOX11 increased between 0.5- and 2-fold, 2
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
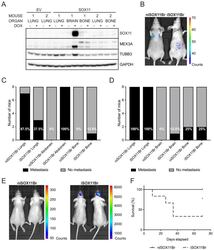
- Experimental details
- Figure 5. SOX11+ DCIS cells isolated from brain metastasis display a colonisation and growth advantage after intracranial xenografting. ( A ) Western blot of SOX11, MEX3A and TUBB3 in total cell lysates of EV and SOX11 cell lines isolated from primary metastasis at indicated sites in presence or absence of DOX. ( B ) Representative in vivo IVIS imaging 7 days after tail vein injections of iSOX11 cells that were isolated from the brain metastasis (SOX11Br) in presence or absence of DOX. ( C ) Tabulated results of micrometastasis from in vivo IVIS imaging 7 days after tail vein injections of SOX11Br cells. ( D ) Tabulated results of micrometastasis from ex vivo IVIS imaging of the tail vein injections of SOX11Br cells. ( E ) IVIS imaging of mice fed normal chow or DOX-containing chow 10 days after intracranial injections of SOX11Br cells. ( F ) Survival curve for mice shown in E. *p = 0.0195. DOX: doxycycline.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
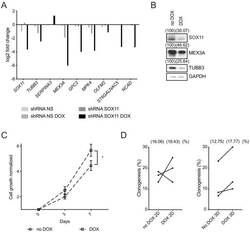
- Experimental details
- Figure 6. SOX11 regulates growth of ER- breast cancer cells. ( A ) qRT-PCR results for several potential SOX11 targets in CAL-148 cells transduced with shRNA to SOX11 or shRNA NS cells with and without DOX induction in cells grown in 2D. ( B ) Western blot of SOX11, MEX3A and TUBB3 in total cell lysates of CAL-148 cells transduced with shRNA SOX11 in presence or absence of 1 muM DOX after 48 hr. GAPDH was used as loading control. Densitometry results normalised against no DOX are shown in brackets. ( C ) Cell growth assay results for CAL-148 shRNA SOX11 cells induced with 1 muM DOX at 3 and 7 days. Experiments were performed three times. Error bars represent SEM. *p=0.0106 (day 7). ( D ) Quantification of clonogenicity in 2D and 3D from single CAL-148 shRNA SOX11 cells plated in presence or absence of DOX after 21 days. The number in brackets represents the mean in each group of the three experimental replicates. DOX: doxycycline, NS: non-silencing.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
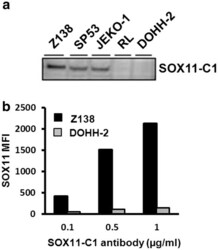
- Experimental details
- Figure 1 Western blot and flow cytometry based evaluation of SOX11-C1 antibody. ( a ) WB analysis revealed a single band at predicted size in SOX11 positive compared to negative cell lines. ( b ) Flow cytometry analysis using SOX11-C1 monoclonal antibody showed specific staining of SOX11 positive compared to negative cells lines over a range of concentrations.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Figure 3 Flow cytometry-based assessment of SOX11 status in cell lines. Assessment of SOX11 status using flow cytometry analysis (bars) of B cell lymphoma and EOC cell lines reveal specific staining in cell lines positive for SOX11, including Z138, GRANTA 519, SP53, JEKO-1, REC-1, BJAB, KM3, OVCAR-3 and TOV-112D as assessed by RT-PCR analysis (diamonds). For each cell line, SOX11 DeltaMFI was calculated as the difference between the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) from SOX11-C1 antibody and the MFI from the control. (MFI SOX11 - MFI control ). The relative SOX11 expression was calculated by scaling all data to the cell line with the lowest DeltaMFI (DOHH-2).
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
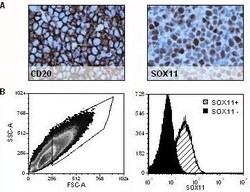
- Experimental details
- Figure 4 Assessment of NSG mouse derived tumors. Tumors established in NSG mice after intravenous injection of Z138 MCL cells were analyzed for specific SOX11 expression. ( A ) IHC-P staining showed a human B cell phenotype (CD20) and confirmed nuclear staining of SOX11. ( B ) Flow cytometry analysis separated SOX11 positive and negative cells, derived from two separate tumors established in NSG through injection of knocked (SOX11 - ) and unknocked (SOX11 + ) Z138 cells.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
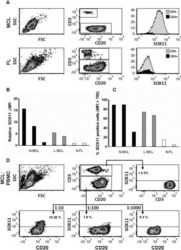
- Experimental details
- Figure 6 Flow cytometry-based assessment of the detection sensitivity of SOX11 in primary MCL cells. Flow cytometry-mediated analysis of SOX11 ( a ) showed that MCL cells were specifically stained compared to infiltrating T cells (MCL CD3+ ) and SOX11-negative malignant cells (FL CD3- ). The specificity of the staining was assessed by comparing ( b ) the relative Delta MFI and ( c ) the fraction of SOX11 positive cells for each patient sample. Both nodal and leukemic cases of MCL were separated from FL using the SOX11 staining. ( d ) The sensitivity of the SOX11 staining was estimated by diluting (1:1, 1:10. 1:100 and 1:1000) L-MCL cells in PBMC.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry