Antibody data
- Antibody Data
- Antigen structure
- References [28]
- Comments [0]
- Validations
- Other assay [6]
Submit
Validation data
Reference
Comment
Report error
- Product number
- 33-5500 - Provider product page

- Provider
- Invitrogen Antibodies
- Product name
- SPARC Monoclonal Antibody (ON1-1)
- Antibody type
- Monoclonal
- Antigen
- Other
- Description
- Source: Monoclonal antibody was obtained by fusing the mouse myeloma cell-line P3-X63-Ag8-U1 with spleen cells of BALB/c mouse after immunization with bovine bone osteonectin (SPARC). The monoclonal antibody was harvested from ascitic fluid. Specificity: This antibody reacts with both bone derived and platelet derived Osteonectin (ELISA). This antibody does not react with non-activated platelet and reacts with thrombin-stimulated platelet (flow cytometric analysis). This antibody reacts with human and bovine Osteonectin (Western blot analysis). This antibody cross reacts with rabbit and porcine Osteonectin. (ELISA) Storage: 4°C. This product does not contain preservative. The stock solution (2.0 mg/mL) should be stored in aliquots at -20°C for 1 year, or should be stored at 4°C for 6 months after adding 0.1% sodium azide. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Reconstitution: Dissolve the lyophilized antibody in 50 µL of distilled water (final concentration: 2.0 mg/mL). This solution can be used as a stock solution. If dilution is necessary for your application, dilute the stock solution with the following Dilution solution just prior to use. When the entire amount of antibody is to be used over a short time period, it may be dissolved directly in 500 µL or more of the Dilution solution. Be sure to store the antibody at a minimum concentration of 2.0 mg/mL. A lower antibody concentration may result in decreased stability. Reconstituted antibody solution should contain 0.1% sodium azide as a preservative when stored at 4°C.
- Reactivity
- Human, Bovine, Porcine, Rabbit
- Host
- Mouse
- Isotype
- IgG
- Antibody clone number
- ON1-1
- Vial size
- 100 µg
- Concentration
- 2.0 mg/mL
- Storage
- 4° C
Submitted references Expression of Extracellular Matrix-Related Genes and Their Regulatory microRNAs in Problematic Colorectal Polyps.
Biochemical and immunohistochemical investigations on bone formation and remodelling in ovariectomised rats with tamoxifen citrate administration.
Effects of formaldehyde on vascular endothelial growth factor, matrix metallopeptidase 2 and osteonectin levels in periodontal membrane and alveolar bone in rats.
Ganoderma lucidum, a promising agent possessing antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects for treating calvarial defects with graft application in rats.
Short-term use of resveratrol in alloplastic graft material applied with calvarial bone defects in rats.
Secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine (SPARC) induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition, enhancing migration and invasion, and is associated with high Gleason score in prostate cancer.
The effect of graft application and simvastatin treatment on tibial bone defect in rats. A histological and immunohistochemical study.
The effect of graft application and allopurinol treatment on calvarial bone defect in rats1.
Diagnostic role of circulating extracellular matrix-related proteins in non-small cell lung cancer.
The effect of different implant biomaterials on the behavior of canine bone marrow stromal cells during their differentiation into osteoblasts.
Attachment and growth of dental pulp stem cells on dentin in presence of extra calcium.
The effect of autologous bone marrow stromal cells differentiated on scaffolds for canine tibial bone reconstruction.
A Magnetic Bead-Based Sensor for the Quantification of Multiple Prostate Cancer Biomarkers.
Stromal Caveolin-1 Is Associated With Response and Survival in a Phase II Trial of nab-Paclitaxel With Carboplatin for Advanced NSCLC Patients.
Vasculogenic mimicry: a new prognostic sign of human osteosarcoma.
Neoplastic and stromal cells contribute to an extracellular matrix gene expression profile defining a breast cancer subtype likely to progress.
Elevated plasma SPARC levels are associated with insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and inflammation in gestational diabetes mellitus.
Stromal responses among common carcinomas correlated with clinicopathologic features.
Effects of bisphosphonates on sutural bone formation and relapse: A histologic and immunohistochemical study.
Markers aiding the diagnosis of chondroid tumors: an immunohistochemical study including osteonectin, bcl-2, cox-2, actin, calponin, D2-40 (podoplanin), mdm-2, CD117 (c-kit), and YKL-40.
A physical mechanism for coupling bone resorption and formation in adult human bone.
Multiple genes are hypermethylated in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas.
The nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug NS398 reactivates SPARC expression via promoter demethylation to attenuate invasiveness of lung cancer cells.
Peritumoral fibroblast SPARC expression and patient outcome with resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
SPARC expression is associated with impaired tumor growth, inhibited angiogenesis and changes in the extracellular matrix.
Gene expression in the normal adult human kidney assessed by complementary DNA microarray.
Gene expression profiling of normal human pulmonary fibroblasts following coculture with non-small-cell lung cancer cells reveals alterations related to matrix degradation, angiogenesis, cell growth and survival.
SPARC/osteonectin is a frequent target for aberrant methylation in pancreatic adenocarcinoma and a mediator of tumor-stromal interactions.
Žlajpah M, Boštjančič E, Tepeš B, Zidar N
Cancers 2020 Dec 11;12(12)
Cancers 2020 Dec 11;12(12)
Biochemical and immunohistochemical investigations on bone formation and remodelling in ovariectomised rats with tamoxifen citrate administration.
Baloğlu M, Gökalp Özkorkmaz E
Folia morphologica 2019;78(4):789-797
Folia morphologica 2019;78(4):789-797
Effects of formaldehyde on vascular endothelial growth factor, matrix metallopeptidase 2 and osteonectin levels in periodontal membrane and alveolar bone in rats.
Laçin N, İzol BS, Tuncer MC, Gökalp Özkorkmaz E, Deveci B, Deveci E
Folia morphologica 2019;78(3):545-553
Folia morphologica 2019;78(3):545-553
Ganoderma lucidum, a promising agent possessing antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects for treating calvarial defects with graft application in rats.
Laçin N, İzol SB, İpek F, Tuncer MC
Acta cirurgica brasileira 2019;34(9):e201900904
Acta cirurgica brasileira 2019;34(9):e201900904
Short-term use of resveratrol in alloplastic graft material applied with calvarial bone defects in rats.
Laçin N, Deveci E
Acta cirurgica brasileira 2019 Sep 12;34(7):e201900704
Acta cirurgica brasileira 2019 Sep 12;34(7):e201900704
Secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine (SPARC) induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition, enhancing migration and invasion, and is associated with high Gleason score in prostate cancer.
López-Moncada F, Torres MJ, Castellón EA, Contreras HR
Asian journal of andrology 2019 Nov-Dec;21(6):557-564
Asian journal of andrology 2019 Nov-Dec;21(6):557-564
The effect of graft application and simvastatin treatment on tibial bone defect in rats. A histological and immunohistochemical study.
Laçin N, İzol BS, Özkorkmaz EG, Deveci B, Tuncer MC
Acta cirurgica brasileira 2019 May 6;34(4):e201900408
Acta cirurgica brasileira 2019 May 6;34(4):e201900408
The effect of graft application and allopurinol treatment on calvarial bone defect in rats1.
Laçin N, İzol BS, Özkorkmaz EG, Deveci B, Tuncer MC
Acta cirurgica brasileira 2019 Mar 18;34(3):e201900306
Acta cirurgica brasileira 2019 Mar 18;34(3):e201900306
Diagnostic role of circulating extracellular matrix-related proteins in non-small cell lung cancer.
Andriani F, Landoni E, Mensah M, Facchinetti F, Miceli R, Tagliabue E, Giussani M, Callari M, De Cecco L, Colombo MP, Roz L, Pastorino U, Sozzi G
BMC cancer 2018 Sep 18;18(1):899
BMC cancer 2018 Sep 18;18(1):899
The effect of different implant biomaterials on the behavior of canine bone marrow stromal cells during their differentiation into osteoblasts.
Özdal-Kurt F, Tuğlu I, Vatansever HS, Tong S, Şen BH, Deliloğlu-Gürhan SI
Biotechnic & histochemistry : official publication of the Biological Stain Commission 2016 Aug;91(6):412-22
Biotechnic & histochemistry : official publication of the Biological Stain Commission 2016 Aug;91(6):412-22
Attachment and growth of dental pulp stem cells on dentin in presence of extra calcium.
Özdal-Kurt F, Şen BH, Tuğlu I, Vatansever S, Türk BT, Deliloğlu-Gürhan I
Archives of oral biology 2016 Aug;68:131-41
Archives of oral biology 2016 Aug;68:131-41
The effect of autologous bone marrow stromal cells differentiated on scaffolds for canine tibial bone reconstruction.
Özdal-Kurt F, Tuğlu I, Vatansever HS, Tong S, Deliloğlu-Gürhan SI
Biotechnic & histochemistry : official publication of the Biological Stain Commission 2015;90(7):516-28
Biotechnic & histochemistry : official publication of the Biological Stain Commission 2015;90(7):516-28
A Magnetic Bead-Based Sensor for the Quantification of Multiple Prostate Cancer Biomarkers.
Jokerst JV, Chen Z, Xu L, Nolley R, Chang E, Mitchell B, Brooks JD, Gambhir SS
PloS one 2015;10(9):e0139484
PloS one 2015;10(9):e0139484
Stromal Caveolin-1 Is Associated With Response and Survival in a Phase II Trial of nab-Paclitaxel With Carboplatin for Advanced NSCLC Patients.
Bertino EM, Williams TM, Nana-Sinkam SP, Shilo K, Chatterjee M, Mo X, Rahmani M, Phillips GS, Villalona-Calero MA, Otterson GA
Clinical lung cancer 2015 Nov;16(6):466-74
Clinical lung cancer 2015 Nov;16(6):466-74
Vasculogenic mimicry: a new prognostic sign of human osteosarcoma.
Ren K, Yao N, Wang G, Tian L, Ma J, Shi X, Zhang L, Zhang J, Zhou X, Zhou G, Wu S, Sun X
Human pathology 2014 Oct;45(10):2120-9
Human pathology 2014 Oct;45(10):2120-9
Neoplastic and stromal cells contribute to an extracellular matrix gene expression profile defining a breast cancer subtype likely to progress.
Triulzi T, Casalini P, Sandri M, Ratti M, Carcangiu ML, Colombo MP, Balsari A, Ménard S, Orlandi R, Tagliabue E
PloS one 2013;8(2):e56761
PloS one 2013;8(2):e56761
Elevated plasma SPARC levels are associated with insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and inflammation in gestational diabetes mellitus.
Xu L, Ping F, Yin J, Xiao X, Xiang H, Ballantyne CM, Wu H, Li M
PloS one 2013;8(12):e81615
PloS one 2013;8(12):e81615
Stromal responses among common carcinomas correlated with clinicopathologic features.
Chen JL, Espinosa I, Lin AY, Liao OY, van de Rijn M, West RB
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2013 Sep 15;19(18):5127-35
Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2013 Sep 15;19(18):5127-35
Effects of bisphosphonates on sutural bone formation and relapse: A histologic and immunohistochemical study.
Oztürk F, Babacan H, Inan S, Gümüş C
American journal of orthodontics and dentofacial orthopedics : official publication of the American Association of Orthodontists, its constituent societies, and the American Board of Orthodontics 2011 Jul;140(1):e31-41
American journal of orthodontics and dentofacial orthopedics : official publication of the American Association of Orthodontists, its constituent societies, and the American Board of Orthodontics 2011 Jul;140(1):e31-41
Markers aiding the diagnosis of chondroid tumors: an immunohistochemical study including osteonectin, bcl-2, cox-2, actin, calponin, D2-40 (podoplanin), mdm-2, CD117 (c-kit), and YKL-40.
Daugaard S, Christensen LH, Høgdall E
APMIS : acta pathologica, microbiologica, et immunologica Scandinavica 2009 Jul;117(7):518-25
APMIS : acta pathologica, microbiologica, et immunologica Scandinavica 2009 Jul;117(7):518-25
A physical mechanism for coupling bone resorption and formation in adult human bone.
Andersen TL, Sondergaard TE, Skorzynska KE, Dagnaes-Hansen F, Plesner TL, Hauge EM, Plesner T, Delaisse JM
The American journal of pathology 2009 Jan;174(1):239-47
The American journal of pathology 2009 Jan;174(1):239-47
Multiple genes are hypermethylated in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas.
Hong SM, Kelly D, Griffith M, Omura N, Li A, Li CP, Hruban RH, Goggins M
Modern pathology : an official journal of the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology, Inc 2008 Dec;21(12):1499-507
Modern pathology : an official journal of the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology, Inc 2008 Dec;21(12):1499-507
The nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug NS398 reactivates SPARC expression via promoter demethylation to attenuate invasiveness of lung cancer cells.
Pan MR, Chang HC, Chuang LY, Hung WC
Experimental biology and medicine (Maywood, N.J.) 2008 Apr;233(4):456-62
Experimental biology and medicine (Maywood, N.J.) 2008 Apr;233(4):456-62
Peritumoral fibroblast SPARC expression and patient outcome with resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
Infante JR, Matsubayashi H, Sato N, Tonascia J, Klein AP, Riall TA, Yeo C, Iacobuzio-Donahue C, Goggins M
Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2007 Jan 20;25(3):319-25
Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2007 Jan 20;25(3):319-25
SPARC expression is associated with impaired tumor growth, inhibited angiogenesis and changes in the extracellular matrix.
Chlenski A, Liu S, Guerrero LJ, Yang Q, Tian Y, Salwen HR, Zage P, Cohn SL
International journal of cancer 2006 Jan 15;118(2):310-6
International journal of cancer 2006 Jan 15;118(2):310-6
Gene expression in the normal adult human kidney assessed by complementary DNA microarray.
Higgins JP, Wang L, Kambham N, Montgomery K, Mason V, Vogelmann SU, Lemley KV, Brown PO, Brooks JD, van de Rijn M
Molecular biology of the cell 2004 Feb;15(2):649-56
Molecular biology of the cell 2004 Feb;15(2):649-56
Gene expression profiling of normal human pulmonary fibroblasts following coculture with non-small-cell lung cancer cells reveals alterations related to matrix degradation, angiogenesis, cell growth and survival.
Fromigué O, Louis K, Dayem M, Milanini J, Pages G, Tartare-Deckert S, Ponzio G, Hofman P, Barbry P, Auberger P, Mari B
Oncogene 2003 Nov 20;22(52):8487-97
Oncogene 2003 Nov 20;22(52):8487-97
SPARC/osteonectin is a frequent target for aberrant methylation in pancreatic adenocarcinoma and a mediator of tumor-stromal interactions.
Sato N, Fukushima N, Maehara N, Matsubayashi H, Koopmann J, Su GH, Hruban RH, Goggins M
Oncogene 2003 Aug 7;22(32):5021-30
Oncogene 2003 Aug 7;22(32):5021-30
No comments: Submit comment
Supportive validation
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
- NULL
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
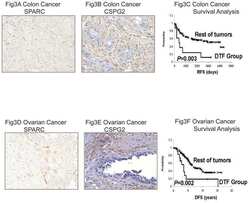
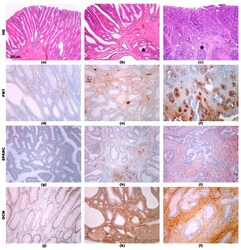
- Figure 2 ( a ) Adenoma; ( b ) adenoma with epithelial misplacement--epithelial misplacement in the submucosa is marked by asterix *; ( c ) adenoma with early carcinoma; invasive carcinoma in the submucosa is marked by asterix *. HE staining, orig. magnification 4x. FN 1: Mild positive reaction in the stroma, mostly in capillaries, in adenoma ( d ). More intensive reaction in the stroma in epithelial misplacement ( e ). Focal reaction in carcinoma cells and in the stroma of invasive carcinoma ( f ). SPARC: Very mild positive reaction in epithelial cells in adenoma ( g ). Mild positive reaction in epithelial cells and focal positive reaction in the stroma in epithelial misplacement ( h ). Mild positive reaction in carcinoma cells and strong positive reaction in the stroma of invasive carcinoma ( i ). DCN: Mild positive reaction in epithelial cells in adenoma ( j ). Mild positive reaction in epithelial cells and strong positive reaction in the stroma in epithelial misplacement ( k ). No positive reaction in carcinoma cells and strong positive reaction in the stroma of invasive carcinoma ( l ). Immunohistochemistry, orig. magnification 10x.
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Fig. 1 ECM related molecules are increased in CAF and selectively released in their conditioned medium: a Western Blot analysis of whole lysates of NF and CAF showing the protein levels of the three molecules (COL10A1, SPARC and COL11A1,) in CAF and NF cell cultures. The histograms show relative quantification by densitometric analysis normalized to Vinculin. b Western Blot analysis for the presence of the proteins COL10A1, SPARC and COL11A1 released in the CM of CAF or NF. The histograms show the densitometric analysis (in arbitrary Units) after normalization with respect to total number of cells. The difference was considered significant at p -value < 0.05
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image

- Experimental details
- Figure 1 Expression of SPARC in biopsy samples of patients with PCa. ( a ) Representative images of IHC against SPARC in TMAs of samples of BPH and PCa of low, intermediate, and high GS. Lower row corresponds to a magnification of the upper images. Scale bars = 100 mum. ( b ) Number of biopsy samples analyzed per group. ( c ) Quantification of DAB signal. The box-plots depict the intensity SPARC signal in each group. Dots outside the box-plot depict the outliers. * P
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
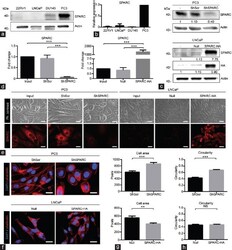
- Figure 2 Basal expression, silencing, and overexpression of SPARC in PCa cell lines. ( a ) Representative image of western blot against SPARC in PCa cell lines 22Rv1, LNCaP, DU145 and PC3. ( b ) RT-qPCR of SPARC in PCa cell lines. DeltaDeltaCt was obtained after normalizing to PUM1 and PC3 cell lines ( n = 3). (c and d) PC3 cells were stable transduced with shRNA against SPARC (ShSPARC) or scramble (ShScr). LNCaP cells were stable transduced with SPARC sequence (SPARC-HA) or an empty vector (). Parental cells (Input) were used as control. ( c ) Representative images of western blot against SPARC in the different cell lines produced. Quantification of optic density was normalized to beta-actin and parental cells, numbers show median ( n = 3). ( d ) SPARC mRNA expression assessed through RT-qPCR ( n = 3); *** P
- Submitted by
- Invitrogen Antibodies (provider)
- Main image
- Experimental details
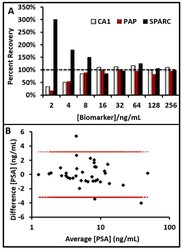
- Fig 3 Serum Validation. A) Percent recovery for three representative biomarkers. Matrix effects can either dampen signal (CA1, PAP) or inflate signal (SPARC). Ideal dilution factors were dependent on sensitivity of the assay and reference range of the biomarker ( Table 1 ). Black dashed line indicates 100% spike recovery. B) Bland-Altman plot [ 38 ] validating specimen integrity of a subset (N = 35) of the clinical samples with high sample volumes. Red dashed line indicates 95% confidence interval.
 Explore
Explore Validate
Validate Learn
Learn Western blot
Western blot Other assay
Other assay